Difference between a Nurse Practitioner and a Doctor
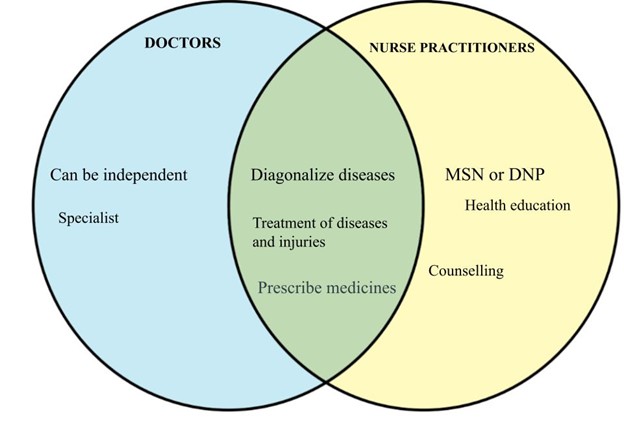
While doctors and nurse practitioners have many things in common, there are some significant differences between these two professions. The one significant difference between the two is the duration of their training time. That is, nurse practitioners receive less training than a doctor. In California, doctors and nurse practitioners are licensed differently. The Nursing Board licenses the nurse practitioners, and the Medical Board licenses medical doctors. Another notable difference is accessibility. Patients can often get appointments to see a Nurse Practitioner quicker than getting to see a doctor.
Nurse Practitioner
A nurse practitioner (NP) is an Advanced Registered Nurse (APRN) with a Master of Nursing (MSN) or Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) certificate. Nurse practitioners have more preparation than registered nurses, and they have responsibilities similar to those of doctors. Nurse practitioners can act as primary or professional nursing staff, usually focusing on specific groups of people, such as families, children, or the elderly. As health personnel, they focus on promoting health and safety education and disease prevention of their patients.
Doctor
Doctors, also known as allopathic doctors, use biological methods for treatment of diseases. Doctors enrolled in medical school and completed specialist training before obtaining their degree. This process requires approximately 11 years of higher education and training, although the time depends on the school program and the country. Almost every critical system of the human body has a specific type of doctor. However, doctors confront the issues of diagnosing and treating diseases, illnesses, injuries, pain, or other human conditions in their area of specialty respectively. They also understand the problem and use their scientific experience to best treat patients with diseases or problems.
| Nurse practitioner | Doctor | |
|---|---|---|
| Certificate | MSN or DNP | Degree in medicine |
| Responsibility | Health and safety education and prevention. | Diagnosis and treatment of diseases |