Differences between American Cheese and Cheddar Cheese
Contents
Differences between American Cheese and Cheddar Cheese
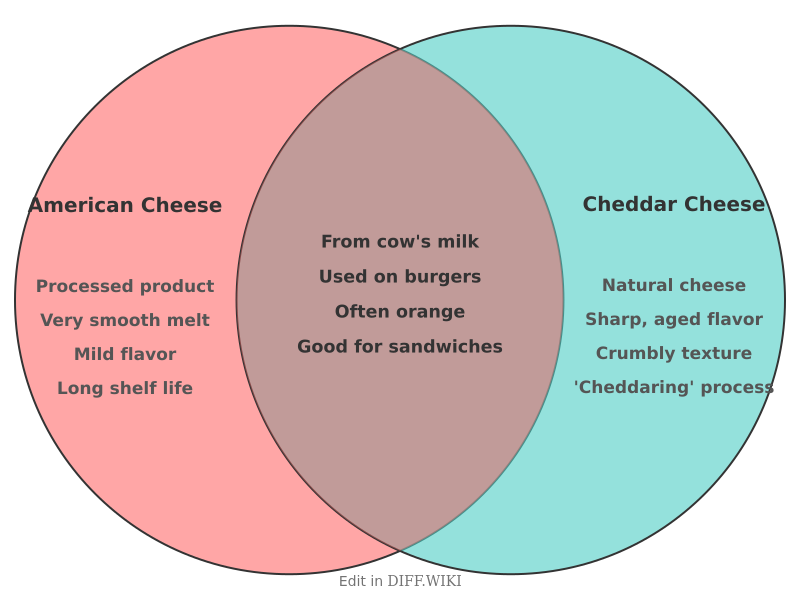
American cheese and cheddar cheese differ substantially in their production, legal definition, and culinary characteristics. Cheddar is a natural cheese made directly from milk, while American cheese is a processed product made from a base of other cheeses, including cheddar.[1][2]
The production of cheddar involves a traditional cheesemaking process where milk is cultured, coagulated with rennet to separate curds and whey, and then put through a unique "cheddaring" process.[3][4] This step involves stacking blocks of curd, which acidifies the cheese and gives it a distinct texture.[3] The cheese is then aged, typically from a few months to several years, which develops its flavor from mild to sharp.[3][5]
American cheese, by contrast, is a processed cheese. Its manufacture begins with grinding and melting at least one type of natural cheese (such as cheddar or colby). According to the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations, the final product must contain a minimum of 51% cheese. Emulsifying agents are added to this cheese base, which prevents the fats from separating when heated and results in a uniform melt. Additional ingredients like milk, cream, salt, and coloring may also be included.[1]
Comparison table
| Category | American Cheese | Cheddar Cheese |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Processed cheese | Natural cheese[1][2] |
| Primary ingredients | A blend of natural cheeses (at least 51%), emulsifying salts, and optional dairy ingredients.[1] | Milk, cheese cultures, rennet, and salt.[3] |
| Flavor | Mild, creamy, and salty.[1] | Varies with age, from mild and milky to sharp, pungent, and nutty.[1] |
| Texture | Smooth, soft, and uniform.[1] | Varies from smooth in young cheddars to firm and crumbly in aged varieties.[1][2] |
| Aging | Generally unaged. | Aged from a few months to multiple years.[3] |
| Melting properties | Melts smoothly and evenly at a low temperature due to emulsifiers.[1] | Can separate and become oily when melted, especially aged varieties.[2] |
Culinary uses
The distinct melting behavior of each cheese influences its common uses. American cheese's ability to melt without breaking makes it a frequent choice for cheeseburgers, grilled cheese sandwiches, and sauces where a smooth, consistent texture is desired.
Cheddar's utility varies with its age. Mild cheddars, which have higher moisture content, melt better than aged versions and are used in cooking. Sharper, aged cheddars have a more complex flavor and a crumbly texture, making them suitable for cheese boards or as a topping where a strong flavor is desired.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "signos.com". Retrieved October 19, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "foodnetwork.com". Retrieved October 19, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "wisconsincheese.com". Retrieved October 19, 2025.
- ↑ "wisconsincheese.com". Retrieved October 19, 2025.
- ↑ "cheddargorgecheese.com". Retrieved October 19, 2025.