Differences between 1080p and 720p
720p vs. 1080p[edit]
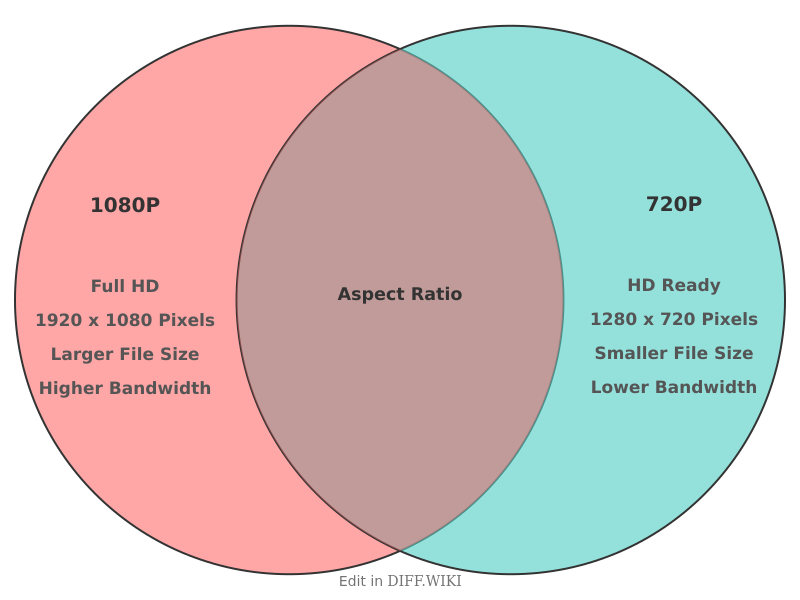
In digital video, 720p and 1080p refer to two common high-definition (HD) display resolutions.[1][2] The number in each term represents the vertical resolution, or the number of horizontal lines of pixels on a screen.[3][4] The "p" stands for progressive scan, a method where all lines of each frame are displayed in sequence, resulting in smoother motion compared to interlaced formats.[5] While both are considered high-definition, 1080p, often marketed as "Full HD," offers a higher pixel count and greater detail than 720p, also known as "HD" or "HD Ready."[3]
The primary distinction between the two resolutions is the total number of pixels.[1] A 720p display has a resolution of 1280 x 720 pixels, totaling 921,600 pixels.[5] In contrast, a 1080p display features a resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels, which amounts to 2,073,600 pixels. This means 1080p has more than twice the pixel information of 720p, allowing for a sharper and clearer image. The higher pixel density of 1080p is particularly noticeable on larger screens or when viewing content with fine details, such as text or intricate graphics.
The choice between 720p and 1080p often involves a trade-off between visual quality and data consumption. Because 1080p video contains more data, it results in larger file sizes and requires more bandwidth for streaming.[3] For instance, streaming a 1080p video can use significantly more data per hour than streaming the same video in 720p. Consequently, 720p can be a more practical option for users with slower internet connections or limited data plans, as it requires less bandwidth to stream smoothly.[2]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | 720p | 1080p |
|---|---|---|
| Common Name | HD, HD Ready[3] | Full HD (FHD)[3] |
| Pixel Dimensions | 1280 x 720[5][2] | 1920 x 1080[3] |
| Total Pixels | 921,600 | 2,073,600 |
| Aspect Ratio | 16:9[5] | 16:9[5] |
| Image Quality | Good; considered standard HD[1] | Sharper and more detailed; higher clarity[1] |
| Bandwidth Requirement | Lower; suitable for slower connections (approx. 3-5 Mbps) | Higher; requires a faster connection (approx. 5-8 Mbps) |
| File Size | Smaller[3] | Larger[3] |
| Typical Use Cases | Mobile devices, smaller screens, data saving[3] | Larger TVs, monitors, gaming, high-quality streaming[3] |
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "seenebula.com". Retrieved October 23, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "lenovo.com". Retrieved October 23, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 "keyla.ai". Retrieved October 23, 2025.
- ↑ "isemc.com". Retrieved October 23, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved October 23, 2025.