Differences between LAN and WAN
Contents
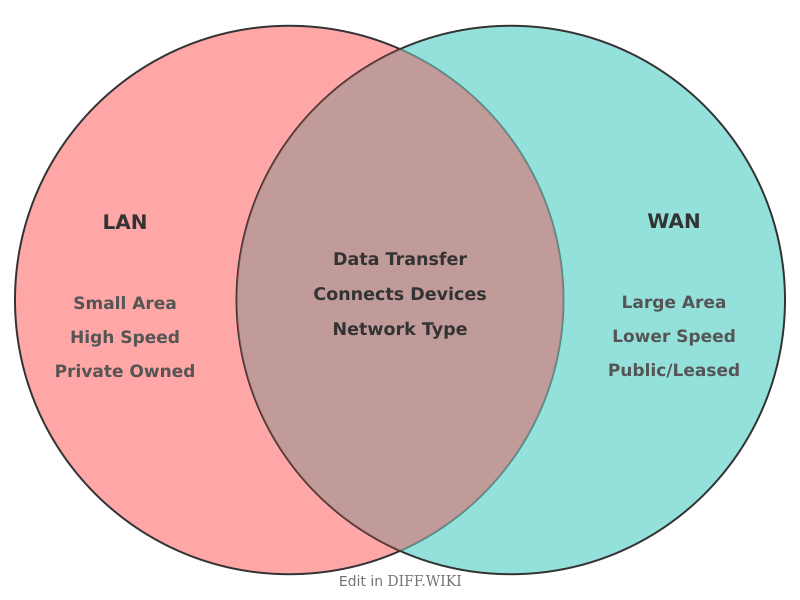
LAN vs. WAN[edit]
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a computer network that connects computers within a limited area, such as a home, school, or office building.[1][2] In contrast, a Wide Area Network (WAN) is a telecommunications network that spans a large geographical area, often connecting multiple LANs. The internet is the largest example of a public WAN.[3]
The primary purpose of a LAN is to facilitate the sharing of resources, such as files and printers, among connected devices in close proximity.[4][5] A WAN's main function is to connect networks over long distances, allowing for communication and data exchange between geographically separated locations. Typically, the infrastructure of a LAN is privately owned and managed by the organization that uses it. WAN infrastructure, however, often involves leased telecommunication circuits and public infrastructure owned by third parties.[3]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Local Area Network (LAN) | Wide Area Network (WAN) |
|---|---|---|
| Geographical Scope | Confined to a small area like a single building or campus.[3] | Spans large geographical areas, connecting across cities, countries, or continents.[3] |
| Speed | Generally offers higher data transfer speeds, with typical rates from 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps. | Typically has lower data transfer speeds compared to a LAN, often limited by the public infrastructure it uses. |
| Infrastructure Ownership | Typically owned, controlled, and managed by a single private organization or individual. | Often utilizes public or leased infrastructure from telecommunication providers.[3] |
| Cost | Lower setup and maintenance costs due to less extensive hardware requirements. | Higher setup and maintenance costs due to the need for routers, leased lines, and other advanced hardware over large distances. |
| Congestion | Experiences less network congestion due to a limited number of connected devices.[4] | More prone to congestion due to the high volume of traffic from multiple connected LANs. |
| Common Technologies | Ethernet (wired) and Wi-Fi (wireless) are the most common technologies used.[1][5] | Technologies include MPLS, VPN, leased lines, and satellite links.[4] |
Security[edit]
LANs are generally considered more secure than WANs because they are isolated within a confined area, allowing for greater control over access and security measures like firewalls.[4] In a WAN, data is transmitted over public or third-party infrastructure, which can increase the risk of interception if not properly encrypted. Technologies such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are often used to enhance security over a WAN by creating encrypted tunnels for data transmission.
Maintenance and Reliability[edit]
The design and maintenance of a LAN are typically simpler and managed in-house. Due to their localized nature, LANs often have higher reliability and fault tolerance.[4] WANs, on the other hand, are more complex to design and maintain, often requiring skilled technicians and network administrators. Their reliance on extensive, often public, infrastructure makes them more susceptible to issues like weather-related outages or third-party technical problems.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved October 25, 2025.
- ↑ "cloudflare.com". Retrieved October 25, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "cloudflare.com". Retrieved October 25, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved October 25, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "builtin.com". Retrieved October 25, 2025.