Differences between GDP and GNP
GDP vs. GNP
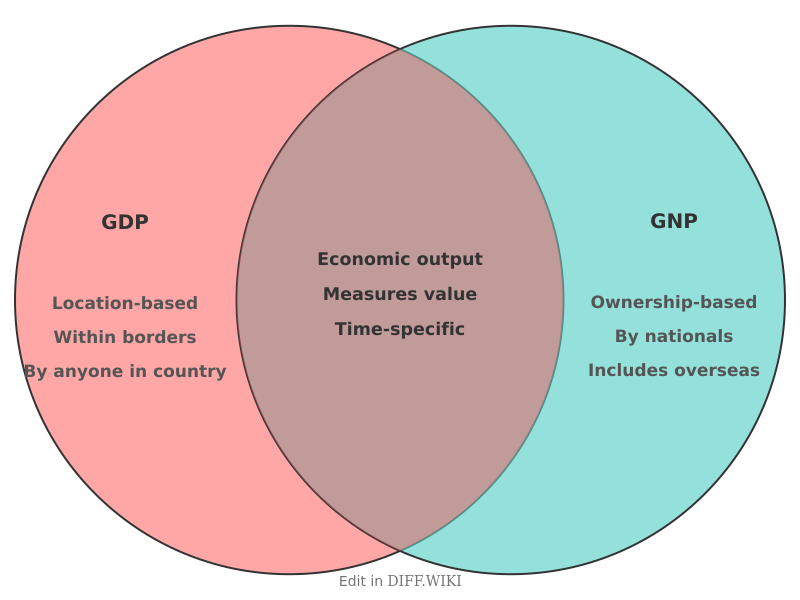
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Gross National Product (GNP) are two of the most common measures used to gauge the economic performance of a country. Both quantify the total market value of all final goods and services produced during a specific period.[1][2] However, they differ in what they consider as part of the economy. GDP measures the value of goods and services produced within a country's geographical borders, by citizens and non-citizens alike.[1][3] In contrast, GNP measures the value of goods and services produced by a country's citizens, both domestically and abroad.[1][3]
The fundamental distinction lies in the basis of calculation: location versus ownership.[4][5] GDP focuses on where the production occurs, while GNP (sometimes referred to as Gross National Income or GNI) focuses on who owns the factors of production.[4][5] For instance, the output of a foreign-owned factory within the United States would be included in the U.S. GDP but not its GNP.[3] Conversely, the profits earned by a U.S.-owned company operating in another country would be counted in the U.S. GNP but not its GDP.[4]
Until 1991, the United States used GNP as its primary measure of economic activity but then switched to GDP. This change was made for two main reasons: GDP corresponds more closely with other domestic economic indicators like employment and industrial production, and it facilitates more direct international comparisons, as most other countries used GDP as their standard.
Comparison Table
| Category | Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | Gross National Product (GNP) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Measures the value of goods and services produced within a country's borders.[1] | Measures the value of goods and services produced by a country's citizens, regardless of location.[1] |
| Basis of Calculation | Location-based: focuses on where the economic activity occurs.[4] | Ownership-based: focuses on who owns the means of production.[4] |
| Inclusion of Foreign Production | Includes production by foreign nationals and foreign-owned companies within the country.[4] | Excludes production by foreign nationals and foreign-owned companies within the country. |
| Inclusion of Citizens' Overseas Production | Excludes income earned by citizens from their investments abroad.[1] | Includes income earned by citizens from their investments abroad. |
| Primary Formula | GDP = C + I + G + (X – M) | GNP = GDP + Net Factor Income from Abroad |
| Main Use | [3]| Analyzing the economic contribution of a country's citizens to the global economy. | |
| Standard International Measure | The most widely used measure for international economic comparisons. | Used less frequently for international comparisons since many major economies switched to GDP. |
The formula to calculate GDP is typically the expenditure approach: GDP = Consumption (C) + Investment (I) + Government Spending (G) + Net Exports (X − M). GNP[2] is derived from GDP by adding the income earned by a country's residents from overseas investments and subtracting the income earned by foreign residents within the country. This is often summarized as GNP = GDP + Net Factor Income from Abroad.
The difference between a country's GDP and GNP can offer insights into its level of global economic integration. A significant variance between the two figures may indicate a high volume of foreign investment in the country or substantial overseas operations by its citizens. For most large economies like the United States, the difference between GDP and GNP is relatively small. However, for smaller countries with significant foreign investment or large remittances from citizens working abroad, the gap can be more pronounced.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "investopedia.com". Retrieved November 10, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "britannica.com". Retrieved November 10, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "365financialanalyst.com". Retrieved November 10, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved November 10, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "vedantu.com". Retrieved November 10, 2025.