Differences between Ocean and Sea
Ocean vs. Sea[edit]
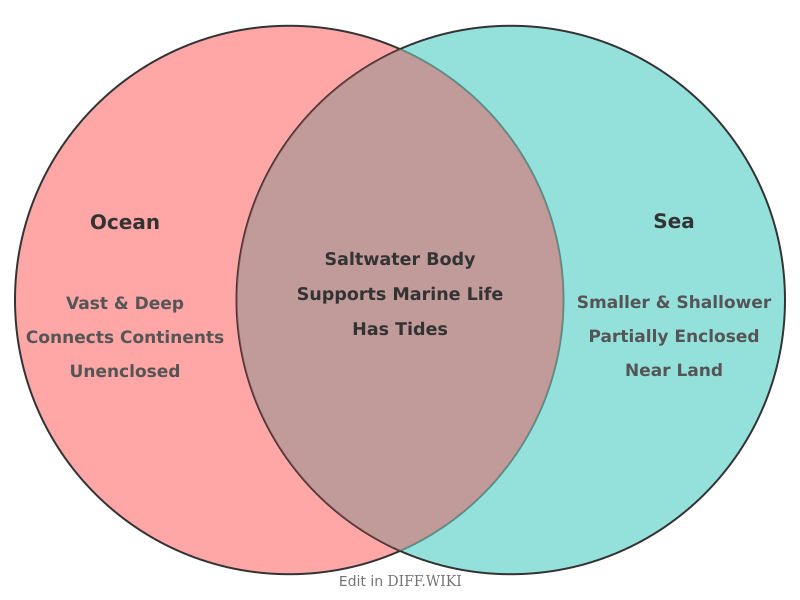
While the terms "ocean" and "sea" are often used interchangeably in common language, geography distinguishes between the two. An ocean is one of the five major divisions of the world's continuous body of saltwater.[1][2] A sea is a smaller body of saltwater, often partially enclosed by land.[3] All seas are part of an ocean.[4]
The primary distinction lies in scale. Oceans are vast, deep bodies of water that cover approximately 71% of the Earth's surface.[5] Seas are generally smaller and shallower than oceans.[4] For example, the Arctic Ocean, the smallest ocean, has a surface area of over 14 million square kilometers, while the largest sea, the Arabian Sea, has a surface area of about 3.6 million square kilometers.
Oceans are the primary bodies of saltwater, and their boundaries are generally defined by continents. There are five recognized oceans: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic. Seas, on the other hand, are typically located where the ocean meets land and are often partially enclosed by it.[3] Examples include the Mediterranean Sea and the Caribbean Sea. An exception is the Sargasso Sea, which is uniquely defined by ocean currents rather than land boundaries.[5][3]
The depth of these bodies of water also differs significantly. Oceans are much deeper than seas.[5] The average depth of the ocean is about 3,700 meters, with the deepest point, the Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean, reaching nearly 11,000 meters. In contrast, the Mediterranean Sea has an average depth of around 1,500 meters.[5]
Marine life is abundant in both oceans and seas, however, the biodiversity is greater in the shallower waters of seas and coastal areas due to the greater penetration of sunlight, which is necessary for photosynthesis.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Ocean | Sea |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Vast, covering large portions of the globe. | Smaller than oceans.[3] |
| Depth | Generally much deeper, with an average depth of around 3,700 meters. | Shallower than oceans.[4] |
| Boundaries | Primarily bounded by continents. | Often partially or mostly enclosed by land.[3] |
| Number | Five recognized major oceans. | Numerous seas around the world. |
| Connection | The primary, continuous body of saltwater. | Smaller parts of an ocean, connected to it.[4] |
| Marine Life | Diverse life at all depths, with many species adapted to extreme pressure and darkness in the deep ocean. | High biodiversity, especially in coastal areas and where sunlight penetrates. |
Legal Definitions[edit]
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) provides a legal framework for the use of the world's oceans and seas. The convention establishes territorial seas, exclusive economic zones, and regulations for international waters, treating the interconnected body of saltwater as a whole for legal purposes. The distinction between an ocean and a sea is not a primary focus of this legal framework.
References[edit]
- ↑ "britannica.com". Retrieved November 14, 2025.
- ↑ "dictionary.com". Retrieved November 14, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "noaa.gov". Retrieved November 14, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "blueplanetaquarium.com". Retrieved November 14, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "britannica.com". Retrieved November 14, 2025.