Differences between PlayStation 3 and PlayStation 4
Contents
PlayStation 3 vs. PlayStation 4
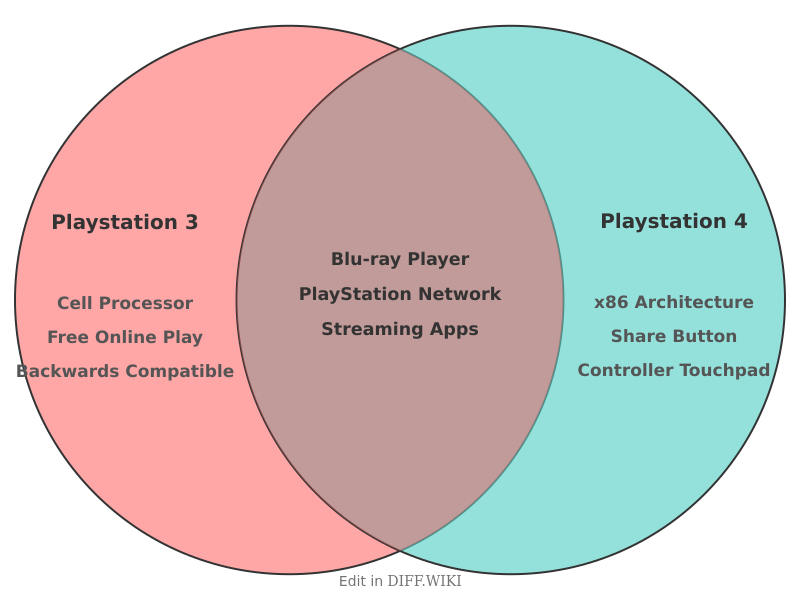
The PlayStation 3 (PS3) and PlayStation 4 (PS4) are home video game consoles developed by Sony Interactive Entertainment, representing the seventh and eighth generations of consoles, respectively. The PS4 was released in November 2013 as the successor to the PS3, introducing significant changes in hardware architecture, controller design, and online services.[1] A primary distinction was the move from the PS3's custom Cell Broadband Engine processor to a more conventional x86-64 architecture in the PS4, similar to that found in personal computers.[2][3] This shift was intended to make game development more straightforward.[4]
A key difference between the two consoles is their approach to backwards compatibility. The PlayStation 4 does not natively support PlayStation 3 games, either from discs or digital downloads.[5] This lack of compatibility is a direct result of the complex and dissimilar processor architectures between the two systems.[3] While some PS3 titles have been made available on the PS4 through remasters or the PlayStation Now streaming service, direct emulation was not technically feasible at the time of the PS4's release.[5]
The user interface also saw a major overhaul. The PS3 utilized the XrossMediaBar (XMB), a menu system featuring horizontally scrolling icons. The PS4 introduced a new interface, the PlayStation Dynamic Menu, designed for easier content discovery and social interaction.
Comparison Table
| Category | PlayStation 3 | PlayStation 4 |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Cell Broadband Engine[2] | 8-core AMD Jaguar x86-64 APU[2] |
| Graphics | 550MHz NVIDIA/SCEI RSX 'Reality Synthesizer'[2] | 800MHz AMD Radeon GCN |
| Memory | 256 MB XDR DRAM, 256 MB GDDR3 VRAM[2] | 8 GB GDDR5[1] |
| Storage | 2.5-inch SATA HDD (user-upgradeable) | 500 GB or 1 TB HDD (user-upgradeable)[1] |
| Controller | DualShock 3 | DualShock 4 |
| Backwards Compatibility | None on later models; early models supported PS2 games | No native support for PS3 games[5] |
| Online Service | PlayStation Network (Free online multiplayer) | PlayStation Network (PlayStation Plus required for most online multiplayer) |
Controller
The controller for the PlayStation 4, the DualShock 4, was a significant redesign from the PlayStation 3's DualShock 3. The DualShock 4 is larger and heavier, with improved ergonomics. It features concave analog sticks for better grip, a clickable touchpad, and a "Share" button for capturing and sharing gameplay content. The L2 and R2 triggers were redesigned for better control. Additionally, the DualShock 4 includes a light bar for motion tracking and player identification, as well as a built-in mono speaker.
Architecture
The most fundamental difference between the PS3 and PS4 lies in their CPU architecture. The PS3 was built around the complex Cell Broadband Engine, a proprietary processor developed by Sony, IBM, and Toshiba.[3] While powerful, it was notoriously difficult for developers to program for.[2] In contrast, the PS4 adopted an x86-64 architecture, specifically a semi-custom Accelerated Processing Unit (APU) from AMD. This shift to a PC-like architecture simplified the development process, allowing for easier creation of multi-platform games. The change in architecture was a primary reason for the PS4's lack of native backwards compatibility with PS3 titles.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved November 22, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "nacongaming.com". Retrieved November 22, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "gamingbolt.com". Retrieved November 22, 2025.
- ↑ "ign.com". Retrieved November 22, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "retrobroker.com". Retrieved November 22, 2025.