Differences between Hinduism and Islam
Contents
Hinduism and Islam[edit]
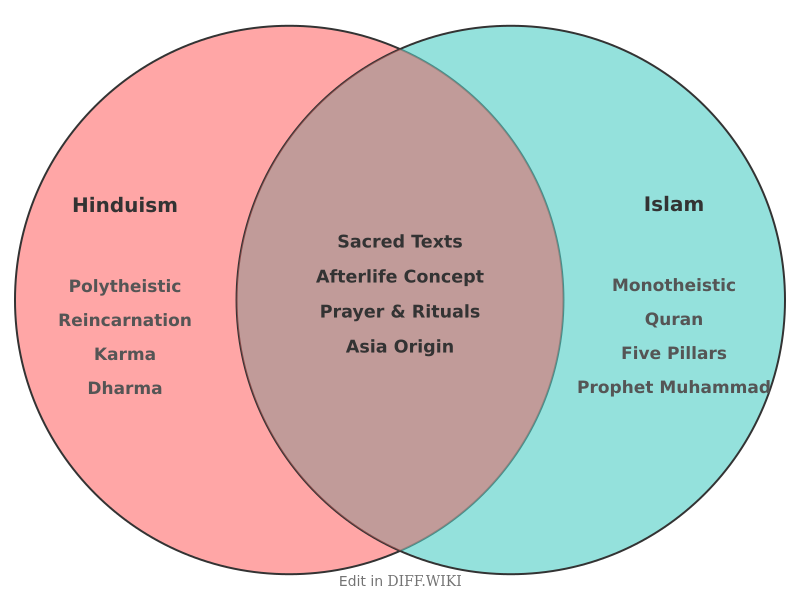
Hinduism and Islam are among the world's largest religions. They possess distinct theological systems and practices that differ on fundamental concepts including the nature of God, scripture, iconography, and the afterlife.[1][2]
Comparison of Beliefs and Practices[edit]
| Category | Hinduism | Islam |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of God | Diverse; can be monotheistic, polytheistic, pantheistic, or henotheistic.[1] Includes the concept of Brahman as the ultimate, formless reality, with deities (Devas and Devis) as manifestations.[2] | Strict monotheism (Tawhid).[1] God (Allah) is one, indivisible, and without partners, a concept central to the faith.[3][2] |
| Principal Figures | Has no single founder. Features divine incarnations (Avatars) like Rama and Krishna, alongside numerous revered sages and gurus (rishis).[4][5] | Believes in a line of prophets sent by God, beginning with Adam. Muhammad is considered the final prophet, who received the Quran.[1] |
| Sacred Texts | A large body of texts, including the Vedas (most authoritative), Upanishads, Puranas, Ramayana, Mahabharata, and Bhagavad Gita. These were revealed to sages over a long period. | The Quran is the central religious text, believed to be the direct and final word of God as revealed to Muhammad. The Hadith, accounts of Muhammad's life and sayings, is also a key source.[1] |
| Iconography (Use of Images) | The use of images and statues (murtis) is a common practice in worship as a way to focus on the divine. These are seen as symbolic representations, not the divine itself. | Strictly aniconic. The use of images or idols to represent God is forbidden and considered the sin of idolatry (Shirk). |
| Concept of Afterlife | Belief in reincarnation (samsara), a cycle of birth, death, and rebirth determined by karma. The ultimate goal is moksha, or liberation from this cycle. Heaven and hell are viewed as temporary states. | Belief in one life on Earth, followed by a Day of Judgment.[1] Individuals are sent to an eternal heaven (Jannah) or hell (Jahannam) based on their deeds and faith. |
| Social Structure | Traditionally associated with a hierarchical caste system (varna and jati), in which social status is determined by birth. | Teaches the equality of all believers before God, with no basis for hereditary social divisions.[5] |
Theology and Divinity[edit]
The core theological principle in Islam is Tawhid, which asserts the absolute oneness and indivisibility of God.[2] Worshipping any other being or object is considered Shirk, the most serious sin.[2] This contrasts with the varied theological framework of Hinduism, which is not defined by a single concept of divinity. Hindu traditions range from monism, where all existence is seen as a single, unified reality (Brahman), to polytheism, where numerous gods and goddesses are worshipped.[1] These deities are often understood as different aspects or manifestations of the supreme Brahman.[2]
Revelation and Authority[edit]
In Islam, the Quran is held to be the direct and unaltered revelation from God to the Prophet Muhammad, serving as the ultimate source of authority.[1] This establishes a clear foundation for doctrine and law. Hinduism does not have a single equivalent text or a final prophet.[1][5] Instead, it draws upon a collection of scriptures known as the Vedas, along with many other texts and teachings from saints and seers, composed and revealed over millennia. Divine guidance is also believed to manifest through avatars, who are earthly incarnations of a deity, such as Vishnu.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "dailygoodmorningkashmir.com". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "jetir.org". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ "muslim-library.com". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ "scribd.com". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "hinduwebsite.com". Retrieved November 23, 2025.