Differences between Converter and Inverter
Converter vs. Inverter
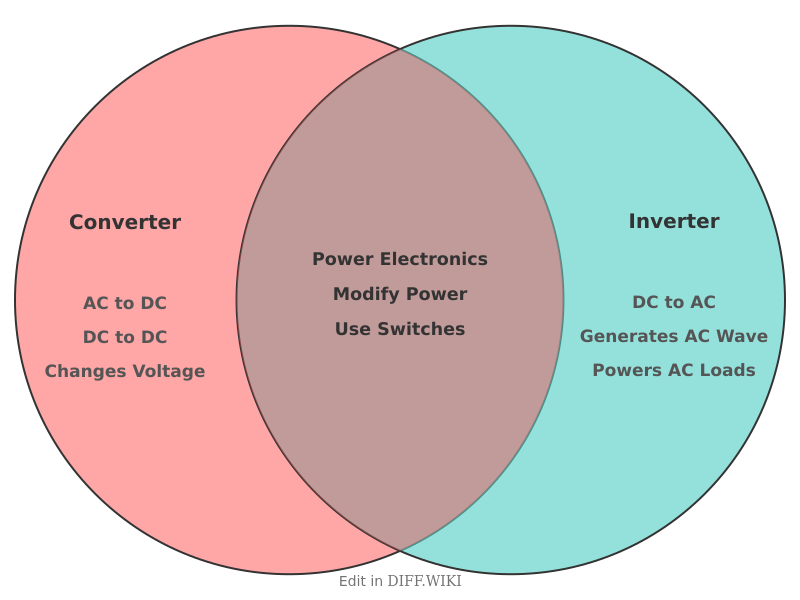
In power electronics, converters and inverters are two distinct devices that alter electrical energy. A converter is a broad term for a device that changes the form of electrical power, which can include modifying voltage or current type.[1][2] An inverter specifically refers to a device that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC).[3][4] While an inverter is technically a type of converter, the terms are not interchangeable and describe different functions in electrical systems.[5]
An AC-to-DC converter, also known as a rectifier, transforms alternating current from a source like a wall outlet into direct current, which is required by most electronic devices. This process involves components like transformers to step down the voltage, diodes to allow current to flow in a single direction, and filters to smooth the resulting DC output. Conversely, a DC-to-DC converter takes an input DC voltage and outputs a different DC voltage level, either higher (boost converter) or lower (buck converter), to match the requirements of a specific load.
An inverter performs the opposite function of a rectifier. It takes a DC power source, such as a battery or solar panel, and converts it into AC power. This is essential for powering standard household appliances and feeding electricity from renewable energy sources into the power grid. The core of an inverter is an electronic circuit, often using transistors, that rapidly switches the direction of the DC input to simulate an AC waveform.
Comparison Table
| Category | Converter | Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Changes the form of electrical energy (e.g., AC to DC, DC to DC). | Converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC).[3] |
| Current Conversion | Can convert AC to DC (rectifier), DC to DC, or AC to AC. | Specifically converts DC to AC. |
| Input Power | Can be AC or DC. | Is always DC. |
| Output Power | Can be AC or DC, depending on the type of converter. | Is always AC. |
| Common Use Cases | Powering electronic devices, charging batteries, and industrial applications like welding. | Solar power systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and powering AC appliances from a DC source like a car battery. |
| Alternative Names | Rectifier (for AC to DC), Chopper (for DC to DC). | DC to AC converter. |
| Core Components | Diodes, transformers, capacitors, inductors. | Transistors (e.g., MOSFETs, IGBTs), control circuits, transformers.[3] |
References
- ↑ "indmall.in". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ "quarktwin.com". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ "bajajfinserv.in". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ "directsolarpower.com". Retrieved November 23, 2025.