Differences between Dictionary and Thesaurus
Contents
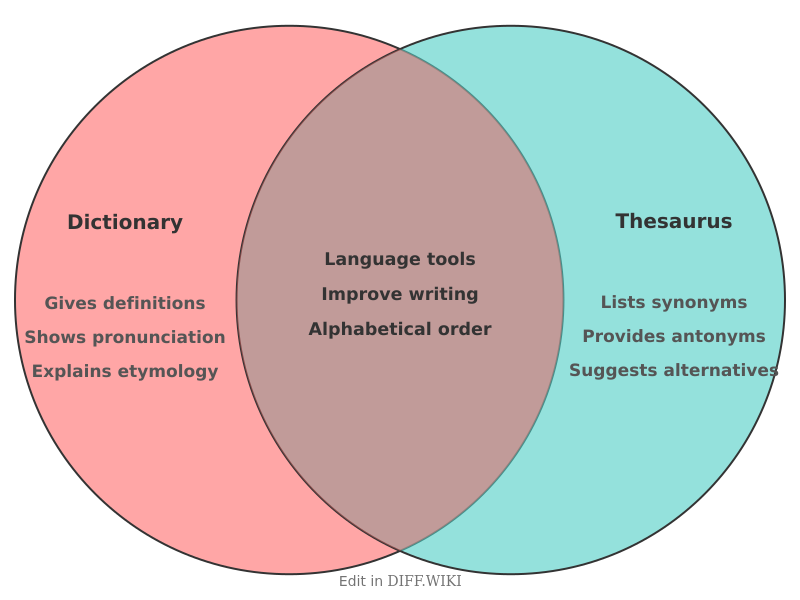
Dictionary vs. Thesaurus[edit]
A dictionary and a thesaurus are both reference works that deal with words, but they serve different primary functions. A dictionary is a book or electronic resource that lists the words of a language in alphabetical order and gives their meaning.[1][2] It often also provides information on pronunciation, origin, and usage.[2][3] In contrast, a thesaurus is a reference work that groups words together based on similarity of meaning.[4] Its main purpose is to provide users with synonyms (words with similar meanings) and often antonyms (words with opposite meanings).[5][4] While a dictionary's goal is to define and clarify, a thesaurus's goal is to offer alternatives and aid in varied expression.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Dictionary | Thesaurus |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | To provide the definition, spelling, and pronunciation of a word.[3] | To provide synonyms and antonyms for a word.[5] |
| Core Content | Meanings, parts of speech, etymology, usage examples.[2][3] | Lists of words with similar or opposite meanings.[3] |
| Use Case | To understand the meaning of an unknown word or verify its spelling. | To find an alternative word to avoid repetition or to express a more precise shade of meaning.[5] |
| Organization | Almost always alphabetical.[1][2] | Can be alphabetical or organized by concepts and ideas. |
| Etymology of Term | From Latin dictionarium, meaning "a collection of words".[2] | From Greek thēsauros, meaning "treasure" or "storehouse". |
| Example for "Happy" | (adjective) Feeling or showing pleasure or contentment. | Joyful, cheerful, merry, delighted, glad. |
Principal Function[edit]
The principal function of a dictionary is to serve as a tool for comprehension. When a reader encounters an unfamiliar word, a dictionary provides its definition, helping to ensure the text is understood correctly. Dictionaries can be either descriptive, documenting language as it is used, or prescriptive, recommending correct usage. Many[1] modern dictionaries also provide historical context by including the etymology, or origin, of a word, which can trace its development over time.
A thesaurus, on the other hand, primarily functions as a tool for expression and literary composition. It is most often used by writers who wish to avoid repeating the same word or who are searching for a word that better fits a specific context, tone, or nuance. For[5] instance, a writer might look up the word "walk" to find alternatives like "stroll", "amble", "trudge", or "march", each carrying a slightly different connotation. While most thesauruses do not provide definitions, some more detailed versions explain the subtle differences between synonyms.
Structure and Content[edit]
A typical dictionary entry is structured to provide a comprehensive overview of a single word. It begins with the headword, followed by its pronunciation (often using the International Phonetic Alphabet), its part of speech, and one or more definitions. Many[3] entries also include example sentences to show the word in context, its inflected forms (such as plurals or past tenses), and its etymological history.
The structure of a thesaurus entry is focused on relationships between words. An entry lists a headword and then provides a set of synonyms. It might also list antonyms. Some[4] thesauruses, particularly those arranged conceptually like the original Roget's Thesaurus, group words into broad categories of ideas rather than a simple alphabetical list. More advanced thesauruses may further categorize synonyms by specific shades of meaning or list related words that are not direct synonyms but are conceptually linked.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "britannica.com". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "englishclub.com". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved November 23, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "editorsweekly.com". Retrieved November 23, 2025.