Differences between Awards and Rewards
Awards vs. Rewards[edit]
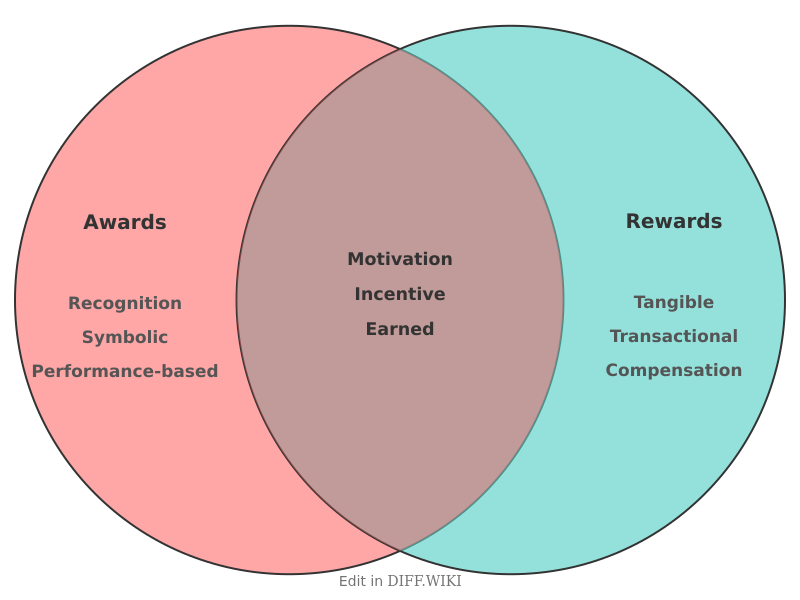
Awards and rewards are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts in recognizing behavior and achievement.[1] An award is a formal recognition bestowed upon an individual or group to honor a specific, often exceptional, accomplishment.[2][3] It serves as a token of excellence in a particular field.[2] In contrast, a reward is something given in return for a person's service, effort, or a desired action.[4][5] It functions as an incentive to encourage and reinforce specific behaviors.[5]
While both are forms of positive reinforcement, their application, formality, and intent differ. Awards are typically tied to significant achievements and are often presented publicly to celebrate success.[1] Rewards can be more informal and are used to acknowledge effort or completion of a task, making them suitable for more frequent application.[5]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Award | Reward |
|---|---|---|
| Basis | Given for exceptional performance, merit, or outstanding achievement. | Given for completing a task, desired behavior, or effort.[5] |
| Nature | Formal and often public, carrying a sense of prestige and honor. | Can be formal or informal, public or private.[1] |
| Purpose | To recognize and honor past excellence and significant accomplishments.[5][2] | To motivate and encourage specific, often ongoing or future, actions and behaviors.[5] |
| Form | Often symbolic and tangible, such as trophies, medals, certificates, or plaques.[2][1] | Can be tangible or intangible, including money, gift cards, praise, or extra time off.[1] |
| Frequency | Typically given less frequently, such as annually or quarterly, often after a selection process.[5] | Can be given frequently, even daily, to reinforce positive actions.[5] |
| Giver | Often decided by a committee, panel of judges, or high-level management.[1][4] | Can be given by anyone, including managers, peers, or the organization itself.[1] |
Psychological Impact[edit]
The psychological effects of awards and rewards are linked to different types of motivation. Awards often appeal to intrinsic motivation by satisfying needs for esteem, a sense of accomplishment, and public recognition. Receiving an award can boost self-esteem and validate an individual's efforts and skills on a broad level. This form of recognition can reinforce a person's identity as a high achiever in their field.
Rewards are more closely tied to extrinsic motivation, where the incentive is an external outcome. The brain's reward system releases dopamine when a reward is received, which creates a feeling of pleasure and reinforces the behavior that led to it.[5] This mechanism makes rewards effective for encouraging the repetition of specific desired actions and achieving short-term goals. While both are valuable, a balanced approach is often considered effective, using awards to celebrate major successes and rewards to encourage consistent positive behavior.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "profit.co". Retrieved November 27, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved November 27, 2025.
- ↑ "vocabulary.com". Retrieved November 27, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "grammar-monster.com". Retrieved November 27, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 "possibleworks.com". Retrieved November 27, 2025.