Differences between FedEx and UPS
Contents
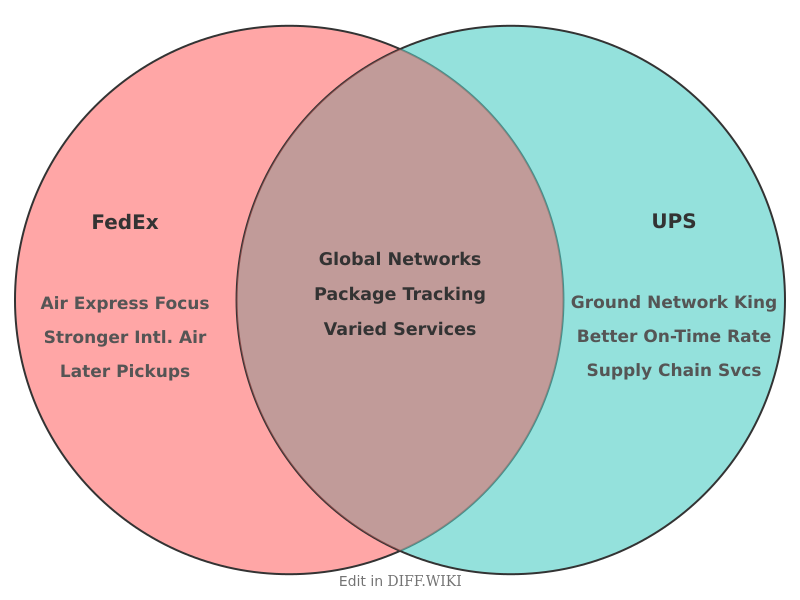
Comparison Article[edit]
FedEx Corporation and United Parcel Service, Inc. (UPS) are two of the largest global courier delivery services. Both American multinational companies are major competitors in the package delivery and logistics industry. FedEx is headquartered in Memphis, Tennessee, while UPS is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia.[1] While both companies offer a wide range of shipping services, they operate with distinctly different business models and network structures.[2][3]
Comparison table
| Category | FedEx | UPS |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Business Model | Operates separate air (Express) and ground (Ground) networks. Ground division uses independent contractors.[4][2] | Utilizes a single, integrated network for both air and ground services with employee drivers.[2] |
| Ground Workforce | FedEx Ground deliveries are handled by independent contractors who own or lease their vehicles.[4][5] | Drivers are direct employees of the company and are represented by the International Brotherhood of Teamsters union. |
| Air Fleet Size | Approximately 700 aircraft in the FedEx Express fleet. | Approximately 291 aircraft in the UPS Airlines fleet. |
| Primary Focus | Known for its air express and overnight delivery services.[2] | Known for its extensive and efficient domestic ground delivery network.[2] |
| Founded | 1971, in Little Rock, Arkansas.[1] | 1907, in Seattle, Washington. |
| Headquarters | Memphis, Tennessee.[1] | Atlanta, Georgia. |
| 2024 Revenue | US$87.7 billion. | US$91.0 billion. |
Business models
The most significant difference between FedEx and UPS lies in their operational structures and labor models.[2]
UPS operates a single, integrated network where one driver, who is a direct company employee, picks up and delivers all types of packages (air and ground) in a given area. The majority of these employees in the United States are members of the Teamsters union, which negotiates collective bargaining agreements covering wages, benefits, and working conditions. This single-network approach is designed for high efficiency in ground package delivery.[2]
FedEx, in contrast, utilizes a multi-network strategy. FedEx Express handles time-sensitive air shipments with employee drivers and pilots, while FedEx Ground specializes in less urgent, day-definite ground deliveries. The FedEx Ground division's model relies on independent contractors, who own or lease their own delivery vehicles and manage their own employees.[4][5] This structure has faced legal challenges regarding the employment classification of its drivers.
Fleet and logistics
The companies' differing operational philosophies are reflected in their fleets. FedEx Express operates one of the world's largest cargo air fleets, with approximately 700 aircraft. This extensive air network supports its focus on overnight and international express shipping.
UPS Airlines operates a smaller fleet of around 291 aircraft. The company's strength is its large and highly efficient ground network, which integrates with its airline to balance speed and cost-effectiveness across its services.[2][3] UPS is a major customer for Boeing's 747-8F freighter, while FedEx is the largest operator of the Boeing 767 freighter.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved December 04, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved December 04, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "investopedia.com". Retrieved December 04, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "businessmodelanalyst.com". Retrieved December 04, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "routeadvisors.com". Retrieved December 04, 2025.