Differences between Fiscal Policy and Monetary Policy
Contents
Fiscal Policy vs. Monetary Policy[edit]
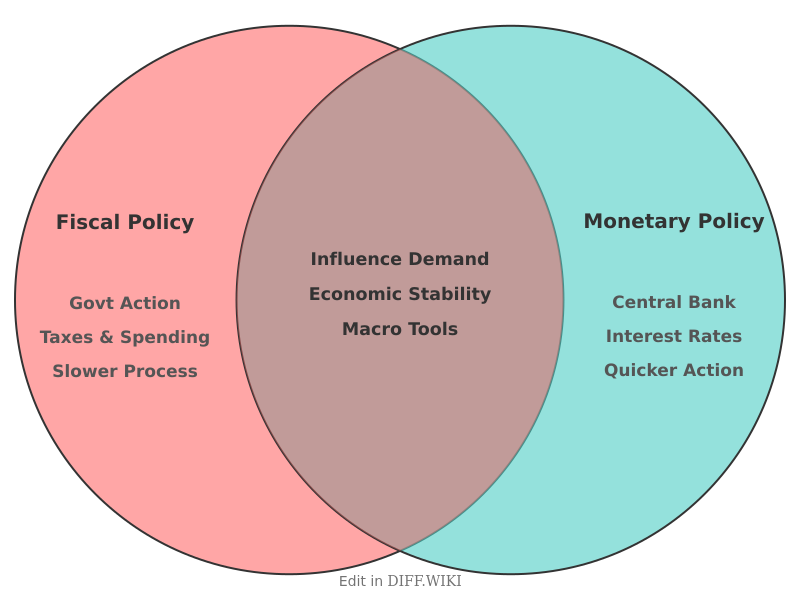
Fiscal policy and monetary policy are two primary macroeconomic tools used by governments and central banks to manage a nation's economy.[1] While both aim to foster economic stability and growth, they differ in their administering bodies, the tools they employ, and the speed at which they can be implemented.[2][3] Fiscal policy involves the use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy, while monetary policy is primarily concerned with managing the supply of money and credit.[1]
In the United States, fiscal policy is determined by the executive and legislative branches of the government.[1][4] Monetary policy, on the other hand, is carried out by the central bank, known as the Federal Reserve (the Fed).[1][4] This separation of powers is intended to shield monetary policy from short-term political pressures.[5]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Fiscal Policy | Monetary Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Administering Body | Government (Legislative and Executive Branches)[1][4] | Central Bank (e.g., U.S. Federal Reserve)[1][4] |
| Primary Tools | Government spending and taxation[1][2] | Interest rates, open market operations, reserve requirements[1][3] |
| Primary Objectives | Economic growth, full employment, price stability | Price stability, maximum employment, stable economic growth[4] |
| Implementation Speed | Generally slower due to legislative processes[2] | Can be implemented relatively quickly[2] |
Fiscal Policy[edit]
Fiscal policy centers on the taxing and spending actions of a government.[1] To stimulate economic activity, particularly during a recession, the government can employ expansionary fiscal policy. This may involve increasing government spending on public works and social programs, or reducing taxes to increase disposable income for consumers and businesses. Conversely, to address high inflation, a government might use contractionary fiscal policy, which involves decreasing government spending or increasing taxes to reduce aggregate demand.
Monetary Policy[edit]
Monetary policy is managed by a country's central bank and focuses on controlling the money supply and interest rates.[3] An expansionary monetary policy aims to increase the money supply and lower interest rates to encourage borrowing and spending, thereby stimulating economic growth. Tools to achieve this include purchasing government securities on the open market, lowering the reserve requirements for banks, and reducing the central bank's lending rate. A contractionary monetary policy, designed to combat inflation, involves selling government securities, raising reserve requirements, and increasing interest rates to decrease the money supply and slow economic activity.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "investopedia.com". Retrieved December 28, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "bitkan.com". Retrieved December 28, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "plus500.com". Retrieved December 28, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "investopedia.com". Retrieved December 28, 2025.
- ↑ "stlouisfed.org". Retrieved December 28, 2025.