Differences between Bluetooth and Wifi
Contents
Bluetooth vs. Wi-Fi[edit]
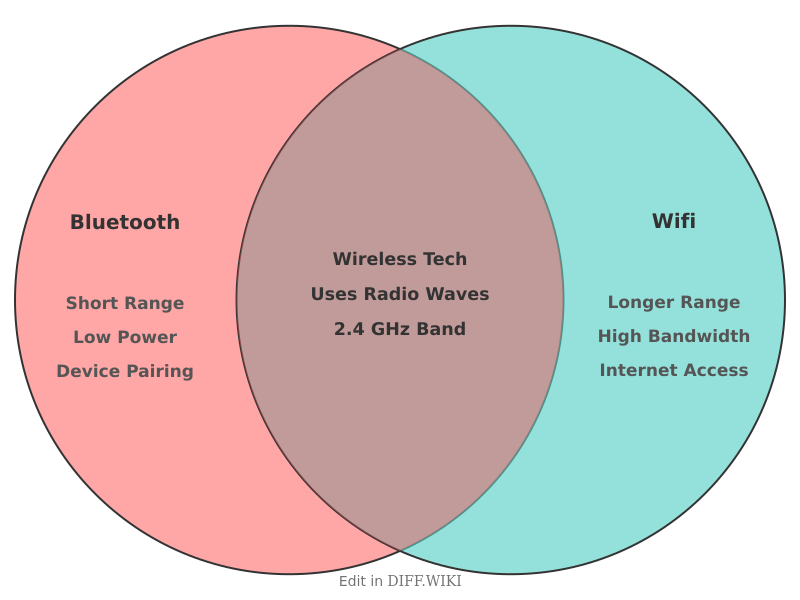
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are both wireless communication standards that use radio waves to transmit data over short distances.[1][2] However, they are designed for different purposes.[1] Bluetooth is primarily used for connecting devices directly to each other in a personal area network (PAN), such as pairing wireless headphones with a smartphone.[3] Wi-Fi, on the other hand, is mainly used to provide wireless access to the internet for multiple devices by creating a wireless local area network (WLAN).[3][2]
The development of these technologies is overseen by different organizations. The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) manages the Bluetooth standard, while the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) creates the 802.11 standards that Wi-Fi is based on. The Wi-Fi Alliance certifies products to ensure interoperability.[2]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Bluetooth | Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Short-range, device-to-device communication (Personal Area Network)[4] | Wireless internet access and local area networking (WLAN)[4][2] |
| Range | Typically up to 10 meters (33 feet), with some classes extending further[5] | Typically 50 to 100 meters (about 160 to 330 feet) |
| Data Transfer Speed | Slower, with rates around 2-3 Mbps for Bluetooth Classic[4] | Faster, with modern standards like Wi-Fi 6 reaching speeds up to 10 Gbps[5] |
| Power Consumption | Low, making it suitable for battery-powered devices | High, as it is designed for higher performance and range |
| Frequency Bands | 2.4 GHz ISM band | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands |
| Device Connections | Typically connects a limited number of devices at once, often in a one-to-one pairing[1] | Can support a large number of simultaneous users connected to a single access point[4][1] |
| Setup | Simple device pairing process | Requires connection to a network access point, often with a password |
Power and Efficiency[edit]
A significant difference between the two technologies is power consumption. Bluetooth is designed for low-power operation, which makes it ideal for small, battery-operated devices like wireless mice, keyboards, and fitness trackers. In particular, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a variant specifically optimized for devices that need to run for long periods on small batteries, such as IoT sensors.
In contrast, Wi-Fi consumes considerably more power to achieve its broader range and higher data transfer rates. This makes it more suitable for devices that have access to a consistent power source, like laptops, smart TVs, and gaming consoles, or where high-speed data transfer is a priority.
Technical Operation[edit]
Both technologies operate in the 2.4 GHz radio frequency band, but Wi-Fi also utilizes the 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands to reduce interference and increase bandwidth. Bluetooth employs a technique called frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS), where the signal rapidly switches between 79 different channels. This method makes Bluetooth connections more resistant to interference from other devices operating in the same frequency band.[3]
Wi-Fi networks operate on specific channels within their frequency bands. To handle data transmission, Wi-Fi breaks down a signal and transmits it across multiple radio frequencies, allowing for higher throughput and enabling multiple devices to use the same transmitter.[1] The standards for Wi-Fi, such as 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), have evolved to support progressively faster speeds and more efficient handling of multiple devices.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "britannica.com". Retrieved January 05, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 05, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 05, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "accsoon.com". Retrieved January 05, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 05, 2026.