Differences between RAM and ROM
RAM vs. ROM[edit]
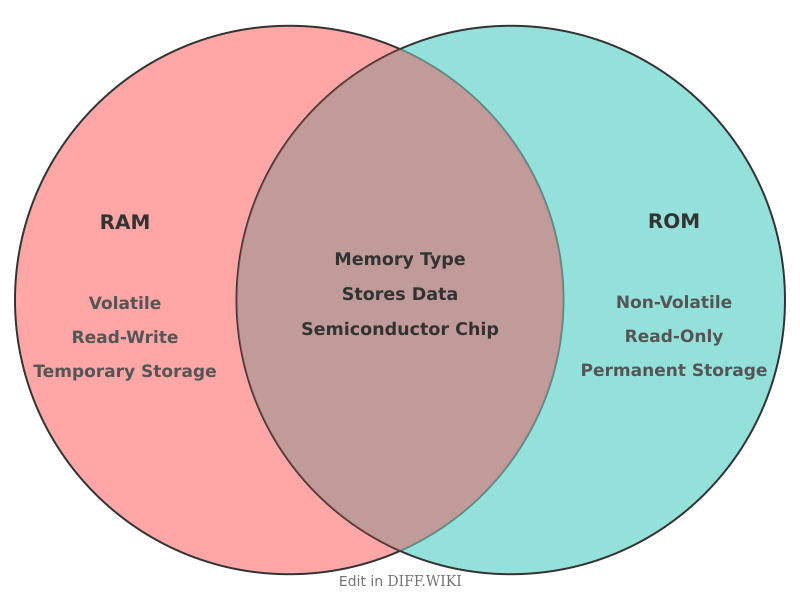
Random-Access Memory (RAM) and Read-Only Memory (ROM) are both forms of semiconductor memory integral to the functioning of computers and electronic devices.[1][2] RAM serves as a volatile, temporary storage space for data that the central processing unit (CPU) is actively using.[3][4] This includes the operating system, applications, and any files currently open.[5] In contrast, ROM is non-volatile memory that permanently stores essential instructions required for the device to operate.[4]
The primary distinction between the two lies in their volatility. RAM requires continuous power to maintain the data it holds; if the power is turned off, its contents are lost. ROM, conversely, retains its stored information even without power, making it ideal for housing firmware and the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) that directs the computer's boot-up sequence.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | RAM | ROM |
|---|---|---|
| Volatility | Volatile; data is lost when power is turned off.[4] | Non-volatile; data is retained without power. |
| Function | Temporarily stores data for active processes and applications. | Permanently stores firmware and boot-up instructions. |
| Data Operations | Read and write operations are supported. | Primarily read-only; data cannot be easily modified.[4] |
| Speed | Significantly faster than ROM, enabling quick data access for the CPU.[4] | Slower than RAM. |
| Typical Capacity | Larger capacity, typically measured in gigabytes (GB). | Smaller capacity, often measured in megabytes (MB). |
| Cost | More expensive per byte than ROM. | Less expensive per byte compared to RAM. |
Types of RAM[edit]
There are two main categories of RAM:
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM) is the most common form of main memory in computers. It stores each bit of data in a separate capacitor within an integrated circuit. DRAM requires a constant refresh of power to maintain the stored information.
- Static RAM (SRAM) is faster and more reliable than DRAM. It stores data using a six-transistor memory cell and does not need to be constantly refreshed. Due to its higher cost and lower density, SRAM is typically used for CPU cache memory.
Modern RAM modules often use Double Data Rate (DDR) technology, with successive generations (DDR3, DDR4, DDR5) offering increased speed and efficiency.
Types of ROM[edit]
While the original form of ROM was permanently written during manufacturing, several variations have been developed:
- Programmable ROM (PROM) can be written to once by a user with a special device.
- Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM) allows its contents to be erased by exposure to ultraviolet light and then reprogrammed.
- Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM) can be erased and reprogrammed electrically, without being removed from the device. This technology is a precursor to modern flash memory.
References[edit]
- ↑ "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 05, 2026.
- ↑ "testbook.com". Retrieved January 05, 2026.
- ↑ "avast.com". Retrieved January 05, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "crucial.com". Retrieved January 05, 2026.
- ↑ "askfilo.com". Retrieved January 05, 2026.