Differences between Electric Heating and Gas Heating
Contents
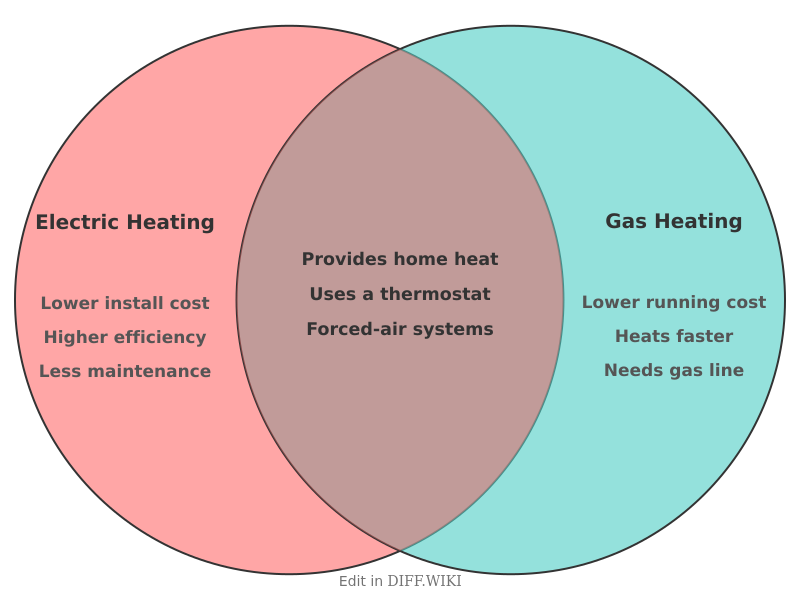
Electric Heating vs. Gas Heating
Electric heating and gas heating are common methods for residential and commercial space heating. The selection between these systems involves considering differences in installation expenses, operational costs, energy efficiency, and environmental effects.[1][2]
Electric heating functions by converting electrical energy directly into heat.[3] This is typically achieved through resistance heating, where an electric current passes through a resistive material, generating heat.[4][5] Common electric heating systems include electric furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps. Gas heating systems burn natural gas or propane to produce heat. In a gas furnace, the combustion of gas heats a component called a heat exchanger. A blower then moves air over the hot heat exchanger, and the warmed air is circulated through the building.
Comparison Table
| Category | Electric Heating | Gas Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Cost | Generally lower, as it does not require gas lines or venting. | Typically higher due to the need for gas line installation and ventilation for exhaust gases.[1] |
| Operating Cost | Often higher because the unit cost of electricity is typically more than natural gas. | Usually lower, as natural gas is often a cheaper fuel source per unit of heat produced. |
| Energy Efficiency (AFUE) | Highly efficient at the point of use, with ratings often between 95% and 100%. | Modern high-efficiency systems can reach up to 98.5% efficiency, though older models are less efficient. |
| Environmental Impact | No direct emissions at the point of use. The overall impact depends on how the electricity is generated.[1][2] | Produces carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases during combustion.[2] |
| Maintenance | Requires less maintenance due to fewer mechanical parts and no combustion process. | Needs regular professional servicing to ensure safety and efficiency, including cleaning burners and checking for leaks. |
| Lifespan | Typically longer, with furnaces lasting 20 to 30 years. | Generally shorter, with furnaces having a lifespan of 15 to 20 years. |
| Safety | No risk of carbon monoxide leaks as there is no combustion. | Carries a risk of carbon monoxide leaks, requiring proper ventilation and detectors.[2] |
Installation and Operating Costs
The initial cost to install an electric heating system is generally lower than for a gas system. Electric furnaces do not require the installation of gas pipes or venting for exhaust, which simplifies the installation process. Gas furnaces, in contrast, necessitate a connection to a gas line and a flue system to vent combustion byproducts, leading to higher upfront costs.[1]
While less expensive to install, electric heating systems often have higher operating costs. The price of electricity per unit of energy is typically greater than that of natural gas. Consequently, the ongoing expense of heating a space with electricity can be higher, though this can vary based on local energy prices. Gas heating is often more cost-effective to run due to the lower price of natural gas.
Efficiency and Environmental Considerations
The efficiency of heating systems is measured by the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE), which indicates the percentage of fuel converted into usable heat. Electric furnaces are highly efficient, with AFUE ratings often approaching 100%, meaning nearly all the electricity consumed is converted to heat. Modern high-efficiency gas furnaces can also be very efficient, with AFUE ratings as high as 98.5%. However, standard or older gas furnaces have lower efficiency ratings.
From an environmental standpoint, electric heating produces no direct emissions at the property. The total environmental impact is dependent on the source of the electricity; if generated from renewable sources, the carbon footprint is low.[2] Gas heating systems burn fossil fuels, which releases carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases directly into the atmosphere.[2]
Maintenance and Lifespan
Electric heating systems generally require less maintenance. Their simpler design with fewer moving parts and the absence of a combustion process reduces the need for frequent servicing. Gas furnaces need regular maintenance by qualified professionals to ensure they operate safely and efficiently. This includes inspecting the heat exchanger, cleaning the burners, and checking for gas leaks.
The typical lifespan of an electric furnace is longer than that of a gas furnace, often lasting between 20 and 30 years. Gas furnaces generally have a service life of 15 to 20 years, as the combustion process can cause more wear on the components over time.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "mayercleaning.co.uk". Retrieved January 08, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "citypowerandgas.com". Retrieved January 08, 2026.
- ↑ "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 08, 2026.
- ↑ "electricradiatorsdirect.co.uk". Retrieved January 08, 2026.
- ↑ "vikingdirect.ie". Retrieved January 08, 2026.