Differences between Amoxicillin and Penicillin
Contents
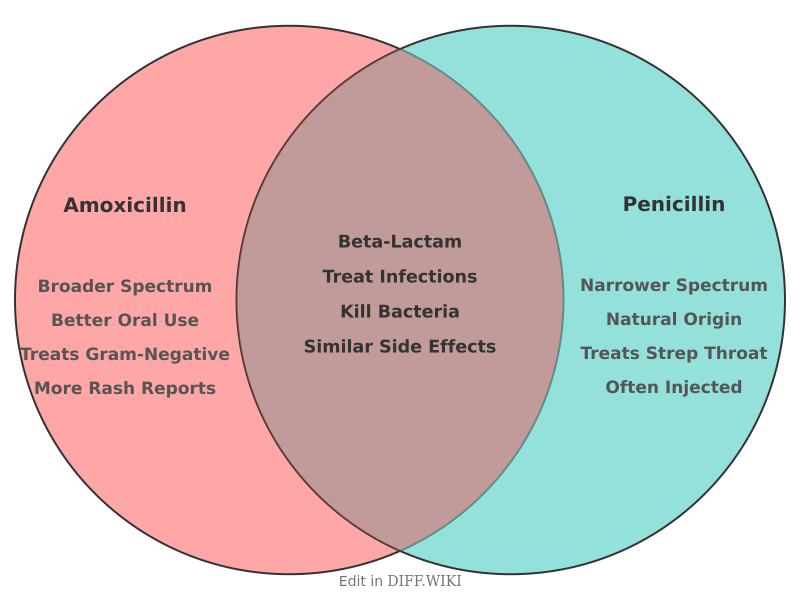
Differences between Amoxicillin and Penicillin[edit]
Amoxicillin and penicillin are both beta-lactam antibiotics used to treat bacterial infections.[1] Amoxicillin is a derivative of penicillin and belongs to the aminopenicillin family of antibiotics.[2] It was developed by chemically modifying the original penicillin structure to improve its effectiveness.[3] Both drugs function by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, which leads to the death of the bacteria.[4] While they share a common mechanism, their structural differences result in distinct properties affecting their range of activity and clinical use.[1]
Comparison table[edit]
| Category | Amoxicillin | Penicillin (Penicillin V/G) |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic Spectrum | Broad-spectrum.[5] Effective against many gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria such as H. influenzae and E. coli.[2] | Narrow-spectrum.[5] Primarily effective against gram-positive bacteria like Streptococcus.[5] |
| Chemical Structure | A penicillin core with an added amino group and a hydroxyl group on its side chain.[1] | A natural or semi-synthetic antibiotic with a core penicillin structure.[3] |
| Oral Absorption | Well-absorbed when taken orally, with bioavailability between 74% and 92%. Absorption is not significantly affected by food. | Penicillin V is acid-stable for oral use, but has variable bioavailability (25% to 60%). Penicillin G is largely destroyed by stomach acid and is typically given by injection.[3] |
| Common Uses | Respiratory tract infections, ear infections, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and H. pylori eradication.[5] | Strep throat, dental infections, and rheumatic fever prophylaxis.[5] |
| Year of Medical Use | 1972.[5] | Widespread use began during World War II, following its discovery in 1928.[5] |
| Resistance | Can be rendered ineffective by beta-lactamase enzymes produced by some bacteria; often combined with clavulanic acid to overcome this.[5] | Susceptible to beta-lactamase enzymes.[2] |
Chemical structure[edit]
Amoxicillin is a semi-synthetic aminopenicillin.[2] Its structure is different from that of penicillin G due to the addition of a hydroxyl group on the phenyl side chain.[1] This modification increases the drug's ability to penetrate the outer membrane of some gram-negative bacteria, which expands its spectrum of activity.[1]
Spectrum of activity[edit]
The structural differences between the two antibiotics directly impact the range of bacteria they can treat. Penicillin is considered a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, mainly targeting gram-positive bacteria.[5] Amoxicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic because it is effective against a wider range of bacteria, including gram-positive bacteria and some gram-negative bacteria such as Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and certain strains of Escherichia coli.[2]
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
A significant difference between the two drugs is their behavior in the body. Amoxicillin is more stable in stomach acid and is absorbed more efficiently and consistently than penicillin V when taken orally. This results in higher concentrations of the drug in the blood. Penicillin V has much more variable oral absorption. Penicillin G is not acid-stable and is usually administered via injection to be effective.[3]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref1 - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref2 - ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref3 - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref4 - ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref5