Differences between Comcast and Verizon FiOS
Contents
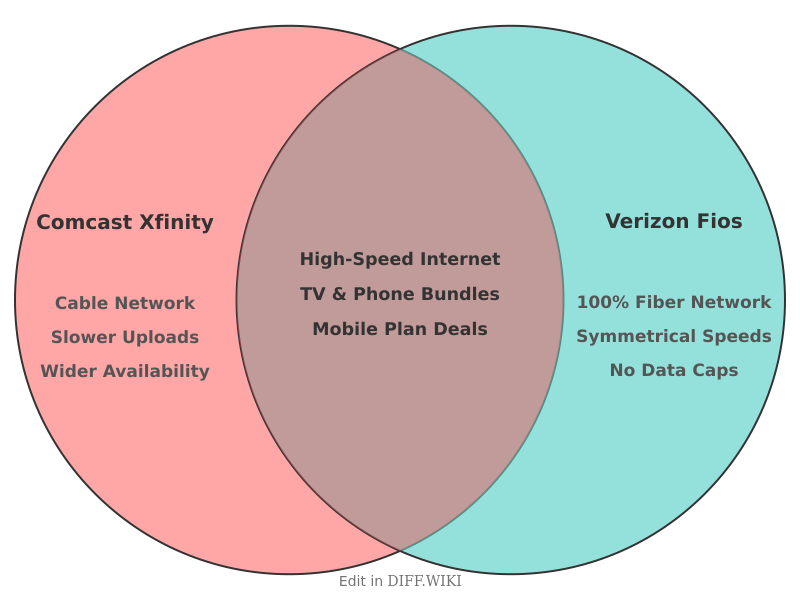
Comcast Xfinity vs. Verizon Fios
Comcast Xfinity and Verizon Fios are two of the largest internet service providers in the United States.[1] The primary distinction between their services lies in the technology used to deliver internet to consumers.[2][3] Verizon Fios operates on a 100% fiber-optic network, while Xfinity primarily utilizes a hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) cable network.[4][2][5][3] This technological difference results in variations in performance, particularly in upload speeds and reliability.[4][2][3]
Availability is another significant differentiator. Xfinity's cable network is accessible in a much larger portion of the U.S. compared to Verizon Fios, which is concentrated mostly in the Mid-Atlantic and New England regions.[4][2] Customer satisfaction surveys tend to rate Verizon Fios slightly higher than Xfinity.[4]
Comparison Table
| Category | Comcast Xfinity | Verizon Fios |
|---|---|---|
| Network Technology | Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC) cable[2][3] | 100% Fiber-optic[4][5] |
| Download Speeds | Up to 2,000 Mbps (2 Gbps) | Up to 2,300 Mbps (2.3 Gbps) |
| Upload Speeds | Asymmetrical; significantly slower than download speeds | Symmetrical; upload speeds are the same as download speeds |
| Data Caps | Historically 1.2 TB in many areas; unlimited data options available. Newer plans may include unlimited data. | No data caps on residential plans |
| Availability | Widely available across roughly 40 states[2] | Limited availability, primarily in nine states in the Northeast U.S.[1] |
| Customer Satisfaction | Generally scores well, but typically below Verizon Fios in direct comparisons[4] | Consistently ranks high in customer satisfaction surveys, often above Xfinity[4][3] |
| TV Service Type | Cable TV | Fiber-optic TV |
Technology and Performance
The core difference impacting performance is network structure. Verizon's use of a fiber-to-the-home connection allows for symmetrical speeds, meaning upload speeds are as fast as download speeds.[2] This is advantageous for activities like video conferencing, uploading large files, and online gaming.[3] Xfinity's HFC network provides fast download speeds but has historically offered much slower upload speeds.[3]
While both providers offer plans with gigabit download speeds, the fiber-optic connection of Fios is often considered more reliable and provides lower latency.[5]
Data Usage Policies
Historically, a key difference was data caps. Verizon Fios does not implement data caps on its standard home internet plans. Comcast Xfinity, for many years, enforced a 1.2 terabyte (TB) monthly data cap in most of its service areas, with overage fees applied for exceeding the limit. Customers had the option to pay an additional fee for unlimited data. However, Comcast has been shifting its strategy, and newer internet packages may include unlimited data without an extra charge.
Service Availability and Bundles
Xfinity has a significantly larger national footprint, making it the available option for a larger number of U.S. households.[4][2] Verizon Fios's fiber network has a more limited, regional presence.[3] Both companies offer service bundles that can include internet, television, and mobile phone services. Xfinity often provides a wider variety of plans and bundle combinations.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "broadbandnow.com". Retrieved January 20, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 "cybernews.com". Retrieved January 20, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 "youtube.com". Retrieved January 20, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 "cnet.com". Retrieved January 20, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "forbes.com". Retrieved January 20, 2026.