Differences between Psychiatry and Psychology
Psychiatry vs. Psychology[edit]
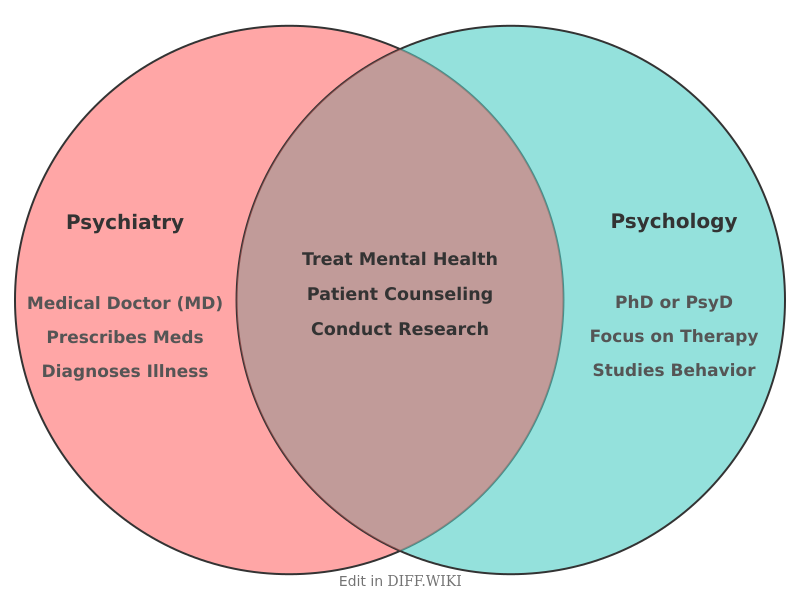
Psychiatry and psychology are distinct fields within mental healthcare, though they often overlap and practitioners may collaborate.[1] Both psychiatrists and psychologists are trained to improve mental well-being and must adhere to a strict code of ethics.[2] The primary distinctions between the two professions lie in their educational backgrounds, scope of practice, and treatment approaches.[3][4]
Psychiatry is a medical specialty focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders.[2][5] Psychiatrists are medical doctors (MDs or DOs) who have completed medical school and a residency in psychiatry. This medical training allows them to prescribe medication and consider the links between mental and physical health. In contrast, psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behavior.[5] Psychologists typically earn a doctoral degree (PhD or PsyD) and their training emphasizes psychotherapy, human behavior, and psychological testing. They are not medical doctors and, in most places, cannot prescribe medication.
The treatment methods employed by psychiatrists and psychologists also differ. Psychiatrists can provide a range of treatments including medication, general medical care, and psychological therapies. They often treat more complex mental illnesses such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and severe depression, where medication is a key component of the treatment plan.[4] Psychologists primarily use psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, to help individuals manage their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.[4] Common therapeutic approaches include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), psychodynamic therapy, and humanistic therapy.[4]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Psychiatry | Psychology |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Biological and neurological aspects of mental illness[4] | Psychological and environmental factors impacting well-being |
| Education | Medical Doctor (MD or DO) with a residency in psychiatry | Doctoral degree (PhD or PsyD) in psychology |
| Prescription of Medication | Yes, can prescribe medication | Generally no, with some exceptions in specific jurisdictions |
| Core Treatment Method | Medication management, often combined with psychotherapy[4] | Psychotherapy (talk therapy) and behavioral interventions[5] |
| Conditions Commonly Treated | Severe or complex conditions like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder[4] | Behavioral problems, learning difficulties, depression, and anxiety |
Collaboration between psychiatrists and psychologists is common in mental healthcare. A psychologist might refer a client to a psychiatrist for medication evaluation, while a psychiatrist may refer a patient to a psychologist for specialized therapy.[4] This team-based approach can provide comprehensive care for individuals with complex mental health needs.[4] Both professionals may work in a variety of settings, including private practices, hospitals, and mental health clinics.