Differences between Advil- and Tylenol
Contents
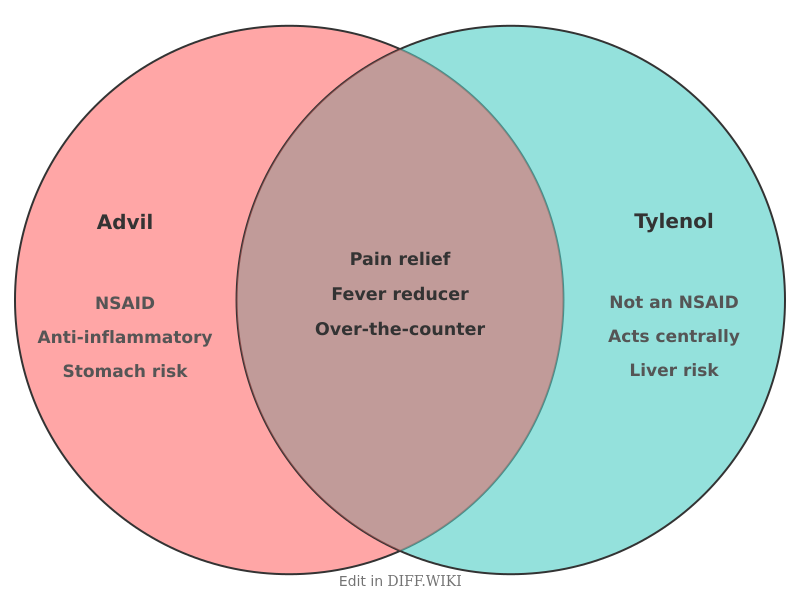
Advil and Tylenol[edit]
Advil and Tylenol are over-the-counter medications used to treat mild to moderate pain and reduce fever.[1][2] Though they treat similar symptoms, they contain different active ingredients and work in different ways.[3] The active ingredient in Advil is ibuprofen, while the active ingredient in Tylenol is acetaminophen.[4][5] Ibuprofen belongs to a class of drugs known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Acetaminophen is classified as an analgesic (pain reliever) and antipyretic (fever reducer).[1][2]
Because of their different classifications, the two medications have distinct mechanisms and recommended uses. Advil is often suggested for pain caused by inflammation, such as menstrual cramps or arthritis, while Tylenol is a common choice for general pain like headaches.[1]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Feature | Advil (Ibuprofen) | Tylenol (Acetaminophen) |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredient | Ibuprofen | Acetaminophen[5] |
| Drug Class | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) | Analgesic and Antipyretic[2] |
| Primary Uses | Relieves pain, reduces fever, and reduces inflammation | Relieves pain and reduces fever[2] |
| Mechanism of Action | Blocks COX enzymes throughout the body to reduce prostaglandins, which cause pain and inflammation | Believed to primarily block COX enzymes in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) to reduce pain signals |
| Anti-inflammatory Effect | Yes, reduces inflammation and swelling | No significant anti-inflammatory effect |
| Common Side Effects | Stomach pain, heartburn, nausea, headache, dizziness | Generally well-tolerated at recommended doses; potential for nausea or headache[1] |
| Major Risks (with overuse) | Stomach ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding, kidney damage, increased risk of heart attack and stroke | Severe liver damage or liver failure |
| Interaction with Alcohol | Increases risk of stomach bleeding | Increases risk of severe liver damage |
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Ibuprofen is an NSAID that works by inhibiting cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes throughout the body. These enzymes are needed to produce prostaglandins, which are chemicals that contribute to inflammation, pain, and fever. By reducing prostaglandin production, ibuprofen helps to alleviate pain and decrease inflammation at the site of an injury.
Acetaminophen's exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it is believed to work primarily on COX enzymes in the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). This action is thought to block pain signals and reduce fever by acting on the heat-regulating center of the brain. Because its activity is concentrated in the central nervous system, it has very little effect on inflammation in the rest of the body.
Clinical Use[edit]
Both medications are effective for treating fever and mild to moderate pain, including headaches, muscle aches, and pain from the common cold.[3] Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, Advil is often recommended for conditions where swelling is a key factor, such as menstrual cramps, arthritis, sprains, and dental pain.[1]
Tylenol is often a preferred option for individuals with stomach issues, kidney problems, or heart disease who may be advised to avoid NSAIDs.[3] It is effective for general aches and pains and does not cause the stomach irritation that can occur with ibuprofen.
Safety and Adverse Effects[edit]
The most significant risk associated with Advil (ibuprofen) is its effect on the gastrointestinal system. It can cause stomach irritation, and with prolonged use or high doses, may lead to ulcers and bleeding. NSAIDs can also impact kidney function and may increase the risk of heart attack or stroke. It is typically recommended to take ibuprofen with food to reduce stomach upset.
The primary safety concern for Tylenol (acetaminophen) is the risk of severe liver damage, or acute liver failure, with overdose. This risk is heightened when consuming alcohol while taking the medication. Because acetaminophen is an ingredient in many combination cold and flu products, unintentional overdose is a notable concern. Acetaminophen overdose is a leading cause of acute liver failure in the United States.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "mercycare.org". Retrieved January 29, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "medlineplus.gov". Retrieved January 29, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "express-scripts.com". Retrieved January 29, 2026.
- ↑ "haleonhealthpartner.com". Retrieved January 29, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "nih.gov". Retrieved January 29, 2026.