Differences between Qualitative and Quantitative
Contents
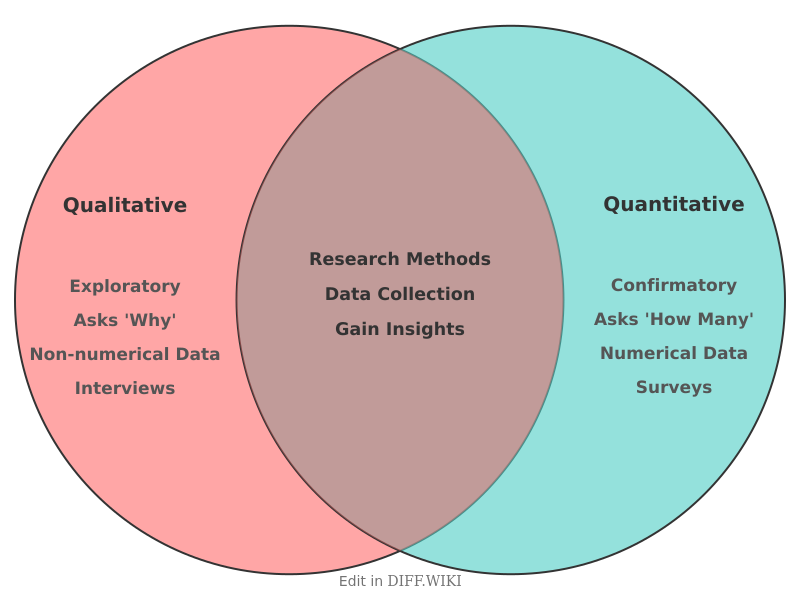
Differences between Qualitative and Quantitative Research[edit]
Qualitative and quantitative research are two primary approaches used in gathering and analyzing data.[1] Quantitative research is centered on numerical data and statistical analysis, often used to test hypotheses and identify patterns.[2][3][4] In contrast, qualitative research focuses on non-numerical data, such as words, images, or observations, to understand concepts, experiences, and meanings in depth.[1][5] The choice between these methods depends on the research question and the type of knowledge sought.[1]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Qualitative Research | Quantitative Research |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To explore ideas, experiences, and meanings.[1] | To test hypotheses, measure variables, and establish relationships.[1] |
| Data Type | Descriptive, non-numerical data (e.g., interviews, observations).[2] | Numerical data that can be measured.[2] |
| Sample Size | Typically small and focused on specific contexts. | Generally involves a large sample size to ensure reliability. |
| Data Collection | Methods include interviews, focus groups, and case studies. | Common methods are surveys, experiments, and structured observations. |
| Data Analysis | Involves thematic analysis, interpretation, and identifying patterns in textual or visual data. | Based on statistical and mathematical analysis to identify trends and relationships. |
| Reasoning | Primarily uses an inductive approach, where theories emerge from the data. | Tends to be deductive, starting with a hypothesis and testing it with data. |
Qualitative Research[edit]
Qualitative research is interpretative and aims to understand the subject from an insider's perspective. It is often conducted in a natural setting, acknowledging that reality is socially constructed. The variables in qualitative research are typically complex and interwoven, making them difficult to measure numerically.
Data collection methods are designed to be open-ended. Common techniques include in-depth interviews, focus groups, and direct observation. The analysis of qualitative data is a systematic process of arranging and interpreting materials to uncover themes and patterns. This approach provides rich, contextual insights into a particular phenomenon.
Quantitative Research[edit]
Quantitative research is characterized by its objective approach to measurement and analysis.[3] It seeks to generalize findings across larger populations.[4] The data collection process is standardized, which allows for replication of the study to compare results.
Surveys with closed-ended questions, controlled experiments, and systematic observations are frequently used to gather numerical data. The analysis involves statistical methods to identify patterns, correlations, or causal relationships. This type of research is valued for its ability to produce reliable and verifiable outcomes.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "scribbr.com". Retrieved February 04, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "simplypsychology.org". Retrieved February 04, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "unimrkt.com". Retrieved February 04, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "voicedocs.com". Retrieved February 04, 2026.
- ↑ "datamation.com". Retrieved February 04, 2026.