Differences between Vitamin B and Vitamin C
Contents
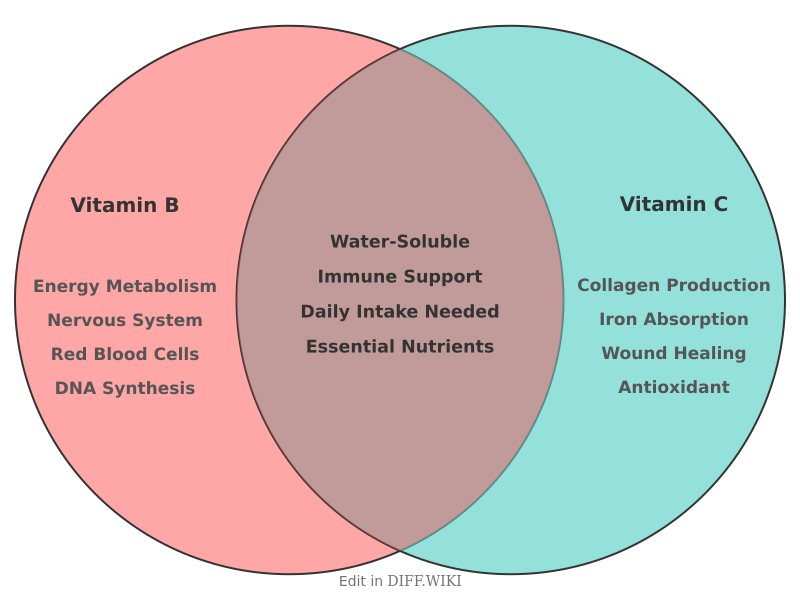
Comparison of Vitamin B and Vitamin C[edit]
Vitamin B and Vitamin C are essential, water-soluble vitamins, meaning the body does not store them in large amounts and excretes excess in urine.[1][2] Daily intake of these vitamins through diet or supplements is therefore necessary to avoid deficiency.[1] While both are vital for human health, they differ significantly in their chemical structure, primary functions, and the health conditions associated with their deficiency.
Vitamin B is not a single vitamin but a group of eight distinct compounds collectively known as the Vitamin B complex.[3] These include B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6 (pyridoxine), B7 (biotin), B9 (folate), and B12 (cobalamin).[4] Together, they perform a wide range of functions, but they are primarily involved in cell metabolism and converting food into energy.[5] They also support healthy skin, nerve function, and the production of red blood cells.[5]
In contrast, Vitamin C is a single compound known as ascorbic acid.[4] Its main functions include acting as an antioxidant that protects cells from damage, supporting the immune system, and aiding in the synthesis of collagen, a protein essential for wound healing, and maintaining the health of skin, bones, and blood vessels.
Key differences[edit]
| Category | Vitamin B Complex | Vitamin C |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | A group of eight chemically distinct vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12).[3] | A single compound known as ascorbic acid.[4] |
| Primary Functions | Energy metabolism, red blood cell formation, nerve function, and cell growth.[3][5] | Antioxidant, collagen synthesis, immune support, and iron absorption. |
| Common Food Sources | Whole grains, meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and leafy green vegetables. | Citrus fruits, peppers, strawberries, broccoli, kiwifruit, and potatoes. |
| Deficiency Diseases | Specific to the vitamin; includes beriberi (B1 deficiency) and pellagra (B3 deficiency). Anemia can result from B12 deficiency. | Scurvy, which can cause fatigue, gum disease, skin bruising, and poor wound healing. |
| Toxicity | Generally low risk, but high doses of some B vitamins, like B6, from supplements can cause nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy). | Low toxicity. However, very high doses (over 2,000 mg daily) can lead to gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and stomach cramps. |
Vitamin B complex[edit]
The B vitamins are a group of nutrients that have a wide range of roles in the body. They are found in a variety of foods, including meat, fish, dairy, eggs, whole grains, and leafy vegetables. While each B vitamin has a unique function, they often work together in metabolic processes. For instance, B12 and folate are both necessary for the production of healthy red blood cells, and a deficiency in either can lead to anemia. Deficiencies in other B vitamins can lead to distinct conditions; a lack of thiamine (B1) causes beriberi, while a niacin (B3) deficiency results in pellagra.
Vitamin C[edit]
Vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, is widely found in fruits and vegetables. Good sources include citrus fruits, bell peppers, broccoli, and strawberries. As an antioxidant, it helps neutralize free radicals in the body. It is also critical for the production of collagen, making it important for the structural integrity of skin, bones, and blood vessels.[4] A severe lack of vitamin C in the diet over an extended period leads to scurvy, a disease characterized by weakness, swollen and bleeding gums, and bruising.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "medicalnewstoday.com". Retrieved February 04, 2026.
- ↑ "bernardshealth.org". Retrieved February 04, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "nih.gov". Retrieved February 04, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "nutrifix-health.com". Retrieved February 04, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "youtube.com". Retrieved February 04, 2026.