Difference Between Angiosperms and Gymnosperms
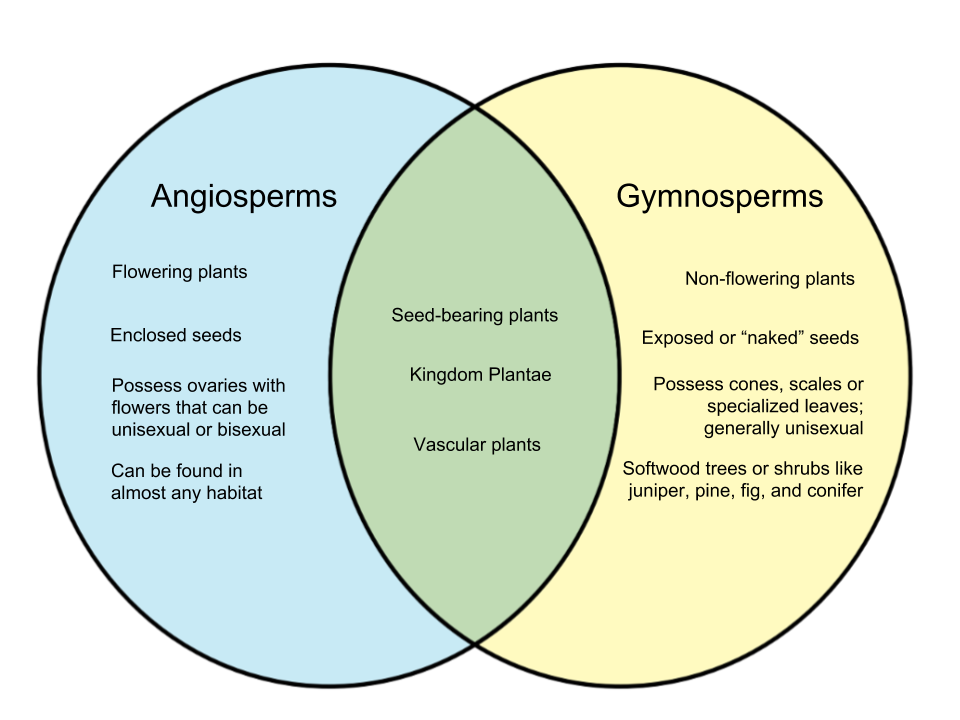
Angiosperms and gymnosperms are two major types of vascular plants (plants that have conducting tissue). Their main distinguishing factor lies in the kinds of seeds they bear, but various characteristics also play a role in their differences. Here, we will discuss the different traits of angiosperms and gymnosperms.
Angiosperms
Angiosperms are commonly called “flowering plants.” They are seed-bearing flowering plants whose seeds are enclosed in flowers or fruits. These plants possess ovaries which may be located in its flowers or fruits, depending on the type. The flowers may either be unisexual or bisexual and rely on different factors to pollinate and reproduce. Angiosperms are diverse and can be found in almost any habitat.
Gymnosperms
Gymnosperms are characterized by their exposed or “naked” seeds. These seeds are located in the surface of specialized leaves. They also tend to develop on the plants’ scales or scones. Gymnosperms are “non-flowering” plants and come in the form of trees and shrubs, although there is one vine that is classified as a gymnosperm. Gymnosperm seeds are found in unisexual cones.
| Angiosperms | Gymnosperms | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seed-bearing, flowering plants whose seeds are enclosed in flowers or fruits | Seed-bearing, non-flowering plants whose seeds are exposed or “naked” |
| Also called | Flowering plants | Non-flowering plants |
| Seeds | Enclosed in an ovary, normally located in a fruit or flower | Unenclosed and can be found in leaves, scales or cones |
| Consists of plants like | Flowering plants, ornamental plants, fruit-bearing plants and trees, vegetables | Conifers, junipers, pines, cedars, firs, cypress trees |
| Reproductive system | Can be bisexual or unisexual | Generally unisexual, rarely bisexual |
| Seed development | Develops within the ovary of a carpel | Develop on the megasporophyll |
| Life cycle | Seasonal | Evergreen |
| Wood | Hardwood | Softwood |
| Leaves | Flat | Scale or needle-like |
| Sporophylls | Accumulate to make flowers | Accumulate to make cones |
| Means of reproduction | Mostly through animals | Relies mostly on the wind |