Difference Between Omega 3 and Omega 6
Fat is a complex topic. Many people interpret fat in different ways, and sometimes in negative light. However, fat is an essential part of one’s diet and can be found in almost all of the diet regimens used nowadays. Omega 3 and Omega 6 are fatty acids that can be found in many dishes and ingredients and play a role in the human system. In this article, we will discuss Omega 3 and Omega 6, which are fatty acids essential to the human body.
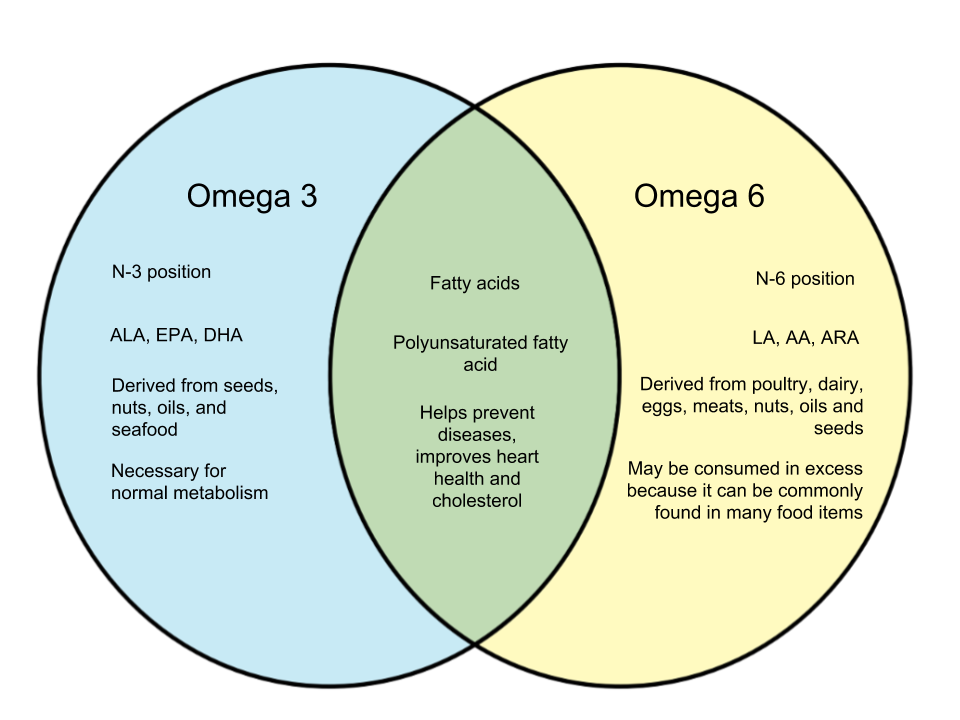
Omega 3
Omega 3 are polyunsaturated fatty acids or PUFAs. There are three types of omega 3 acids in the human system - alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is hard to produce in the human system and can be derived from food from plant forms like canola oil, flaxseed, chia seed, and walnuts. On the other hand, DHA and EPA are the marine forms of Omega 3 and can be found in seafood. Examples of these are oily fishes like salmon, herring and tuna. Omega 3 is important to humans because mammals naturally have difficulty in synthesizing these acids, which are useful for normal metabolism.
Omega 6
Omega 6 are also polyunsaturated fatty acids. Acids under these category include linoleic acid and arachidonic acid. These can be derived from vegetable oils, seeds, nuts, meat and eggs. Omega 6 can be found in many foods such as dairy, eggs, baked goods, and even fast food. Despite the benefits it can give, however, there is a growing concern since people seem to be consuming omega 6 in excess unintentionally. This is because it is so common that it can be found in many dishes like the ones specified above.
| Omega 3 | Omega 6 | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A polyunsaturated fatty acid that plays a role in the optimal function of the human body | A polyunsaturated fatty acid with pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory effects |
| Placement | Final carbon-carbon double bond in the n-3 position (n-3) | Final carbon-carbon double bond in the n-6 position (n-6) |
| Examples/types | Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | Linoleic acid (LA), calendic acid, arachidonic acid (AA, ARA), gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) |
| Can be found in | Fatty fish, oils, nuts, seeds, fish oils | Poultry, dairy, nuts, eggs, cereals, oils |
| Benefits | Protective functions against diseases, heart health, vision, brain health, and cholesterol | Heart health, cholesterol, anti-inflammation, and aid in disease prevention |