Difference between AWD and 4WD
AWD and 4WD are so similar as both are used to send torque to the four-wheel of a vehicle. However, 4WD is outstanding due to its nature which includes strength and function ability in rougher terrains. It is important to note that AWD automatically engages the four wheels, but the 4WD needs to be powered before you can engage the four wheels. Due to the weight of the AWD, the tears and wears off of the tires occur faster; therefore, it is more difficult to maintain than 4WD. AWD also consumes more fuel than 4WD; therefore, it is more expensive to use when compared to 4WD. For extreme weather conditions like snow during winter, It's advisable to use 4WD due to its robustness and ability to work well with rough terrains. But if anyone insists on AWD or 4WD on snowy and icy roads, it's better to use winter tires or use snow chains to prevent easy wearing and tearing of the tires and be able to drive well on the icy road and prevent slipping of tires.
AWD
An all-wheel drive is a type of driver feature that can power all four-wheel wheels of a vehicle automatically. It controls both the front and rear wheels of a vehicle. The AWD is significant and costly to use due to its oil-consuming ability. Because the AWD controls all four wheels, there is less slipping of tires, and the driver has more control of his vehicle
4WD
The four-wheel-drive (4WD) is a double axle drive train that needs to be engaged before it controls the four-wheel of a vehicle. Due to its robustness, it is suitable for offloaders with low-range gearing. They come in two types; full-time and part-time, with both types able to handle rough terrains.
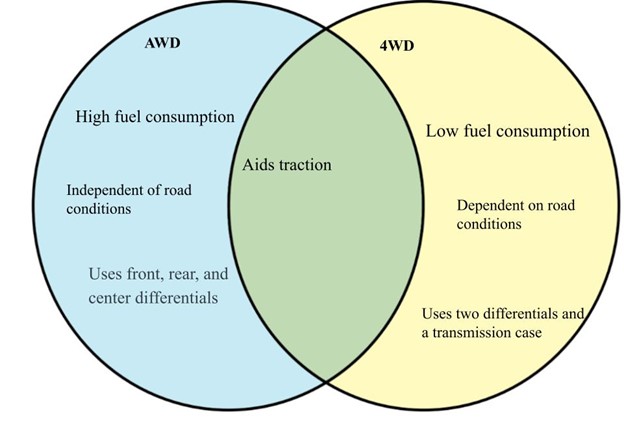
| AWD | 4WD | |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel consumption | High | Low |
| Power distribution | It uses rear, front and center differentials to distribute power and torque. | Uses two differentials and a transmission case to distribute power and torque. |
| Where does power goes? | Power is transferred to the wheels that require the most traction. | Power is distributed between the front and rear axles so that the torque is evenly distributed between all four wheels. |
| Traction | 4-wheel drive regardless of road conditions. | Power to 2 or 4 wheels, based on the road conditions. |
| Dependency | Independent of road conditions. | Dependent on road conditions. |