Differences between Addiction and Dependence
Contents
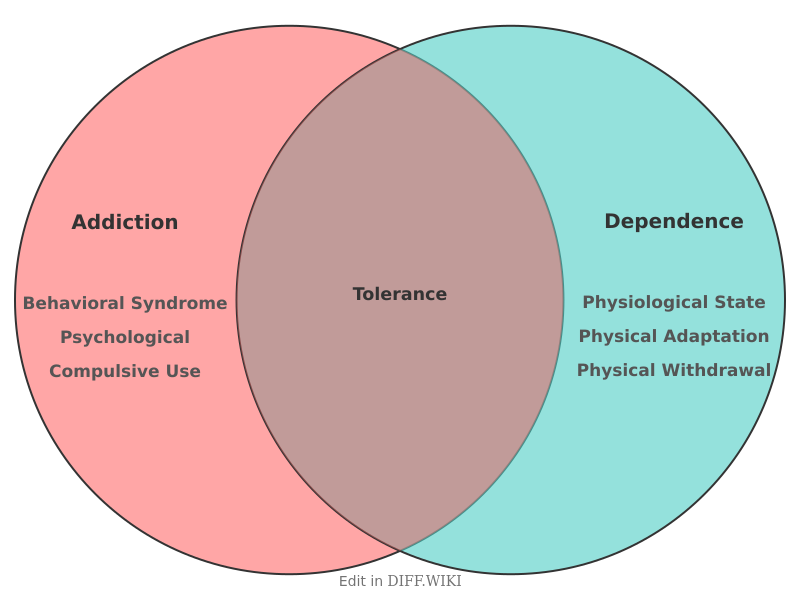
Addiction vs. Dependence
The terms addiction and dependence are often used interchangeably, but they describe different conditions.[1] Dependence refers to a physical state in which the body adapts to a substance, leading to withdrawal symptoms if use is stopped or reduced.[1][2] Addiction is a chronic brain disorder characterized by compulsive substance use despite harmful consequences.[3][4] A person can be dependent on a substance without being addicted, and in some cases, addicted without being physically dependent.[1]
Historically, the terms substance abuse and substance dependence were used. However, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), replaced them with the single diagnosis of "substance use disorder" to reduce confusion.[5] A substance use disorder is diagnosed based on 11 criteria and is graded as mild, moderate, or severe.
Comparison Table
| Category | Addiction | Dependence |
|---|---|---|
| Core Concept | A behavioral syndrome characterized by compulsive use, cravings, and an inability to control use despite negative consequences.[3] | A physiological state where the body adapts to a substance, resulting in tolerance and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation. |
| Nature | Primarily psychological and behavioral, involving changes in the brain's reward circuitry. | Primarily a physical adaptation of the body to the presence of a drug.[1] |
| Withdrawal | May or may not involve severe physical withdrawal symptoms. Cocaine, for example, does not cause major physical withdrawal but is highly addictive. | Characterized by physical withdrawal symptoms when the substance is stopped or reduced. |
| Compulsion | A defining characteristic is the compulsive seeking and use of a substance, even with awareness of its harmful effects.[5][4] | Compulsive use is not a necessary component. A person can be physically dependent on a prescribed medication without being compelled to misuse it.[1] |
| Tolerance | Often a feature, where increasing amounts of a substance are needed to achieve the same effect.[3] | A key indicator of dependence, as the body adapts to the substance. |
Physical and Psychological Aspects
Dependence can be both physical and psychological. Physical dependence manifests through the physiological symptoms of withdrawal when a substance is discontinued. This is a natural bodily response to the prolonged presence of certain drugs, including many prescribed medications.
Psychological dependence involves an emotional or mental reliance on a substance, often tied to specific triggers such as stress or social situations.[1] Addiction is considered a psychological state, where a person compulsively seeks a substance due to powerful cravings and changes in the brain, regardless of physical dependence. For example, a person may be physically dependent on a prescribed opioid for pain management without having an addiction, meaning they do not experience cravings or compulsive drug-seeking behavior. Conversely, someone may be addicted to a substance like cannabis or cocaine without significant physical withdrawal symptoms.
Diagnostic Evolution
The DSM-5 moved away from the terms "abuse" and "dependence" toward the broader classification of "substance use disorder" to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the issue. This change helps to clarify that while physical dependence (specifically tolerance and withdrawal) is one of the possible symptoms of a substance use disorder, it is not the sole indicator. The current diagnostic model assesses a spectrum of behaviors and physiological symptoms to determine the severity of the disorder.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "medicalnewstoday.com". Retrieved January 29, 2026.
- ↑ "clevelandclinic.org". Retrieved January 29, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "mayoclinic.org". Retrieved January 29, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "nih.gov". Retrieved January 29, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 29, 2026.