Differences between Bronchitis and Pneumonia
Contents
Differences between Bronchitis and Pneumonia
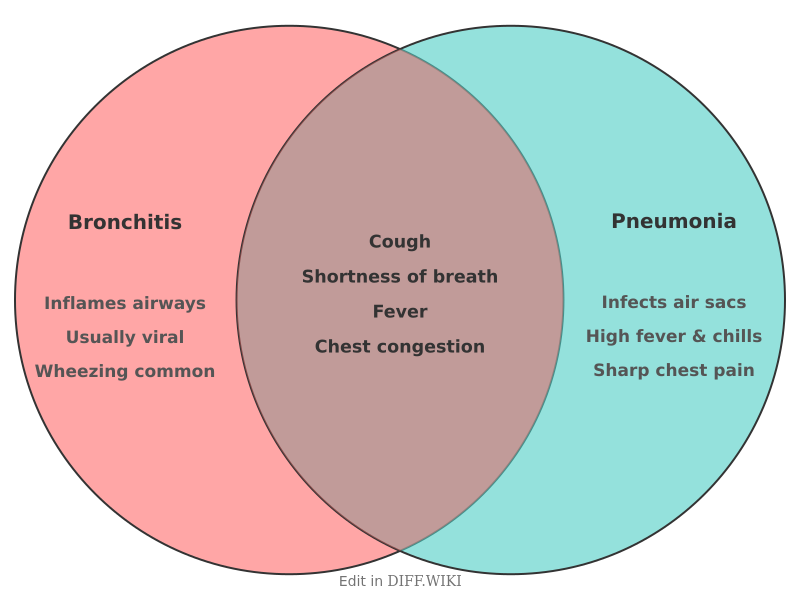
Bronchitis and pneumonia are both lower respiratory tract infections with similar symptoms, such as coughing and difficulty breathing.[1] The primary distinction between the conditions lies in the location of the inflammation.[2][3][4] Bronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs.[5][4] Pneumonia is an infection deeper in the lung tissue, affecting the small air sacs called alveoli, which can fill with fluid or pus.[2][3][4] Pneumonia is generally considered a more serious condition than acute bronchitis and can lead to more severe complications.[5][2][1]
Comparison Table
| Category | Bronchitis | Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|
| Affected Area | Inflammation of the bronchial tubes (airways).[5][4] | Infection of the alveoli (air sacs) within the lungs.[2][3] |
| Common Causes | Primarily viral (e.g., cold or flu viruses).[5] Bacterial causes are less common. | Can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. |
| Key Symptoms | Persistent cough (with or without mucus), chest tightness, wheezing, and often a low-grade fever.[5] | Productive cough (often with yellow, green, or bloody mucus), high fever, shaking chills, and shortness of breath or sharp chest pain.[1][4] |
| Severity | Acute bronchitis is typically less severe and often resolves on its own.[5] | Can range from mild ("walking pneumonia") to life-threatening and may require hospitalization.[5] |
| Diagnosis | Usually diagnosed based on physical exam and symptoms. A chest X-ray is typically normal.[3] | Often confirmed with a chest X-ray, which shows fluid in the air sacs (infiltrates).[3] |
| Treatment | Treatment focuses on symptom relief (rest, fluids, cough suppressants). Antibiotics are not effective for viral bronchitis.[4] | Treatment depends on the cause. Bacterial pneumonia requires antibiotics, while viral pneumonia may be treated with antiviral drugs.[5][1] |
Diagnosis
A physical examination helps in diagnosing both conditions, but differentiating between them can sometimes be difficult based on symptoms alone. A key diagnostic tool is the chest X-ray. In cases of bronchitis, a chest X-ray will typically appear normal because the inflammation is in the airways and not the lung tissue itself.[3] For pneumonia, a chest X-ray is the standard method for confirmation, as it can clearly show inflammation and fluid-filled sacs in the lungs.[3]
Treatment and Complications
Treatment for acute bronchitis, which is most often viral, primarily involves supportive care to manage symptoms while the infection runs its course.[4] Antibiotics are generally not prescribed unless a bacterial infection is suspected.[1] In contrast, bacterial pneumonia requires prompt treatment with antibiotics.[5][1] Antiviral or antifungal medications may be used for pneumonia caused by other organisms.[5]
While acute bronchitis usually resolves without lasting effects, pneumonia can lead to serious complications, including lung abscesses and sepsis, a life-threatening blood infection. Pneumonia is more likely to require hospitalization, especially for young children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems or other chronic health conditions.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref1 - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref2 - ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref3 - ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref4 - ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref5
References
Cite error: <ref> tag defined in <references> has group attribute "" which does not appear in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag defined in <references> has group attribute "" which does not appear in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag defined in <references> has group attribute "" which does not appear in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag defined in <references> has group attribute "" which does not appear in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag defined in <references> has group attribute "" which does not appear in prior text.