Differences between Double-Hung Windows and Single-Hung Windows
Contents
Double-hung windows vs. single-hung windows
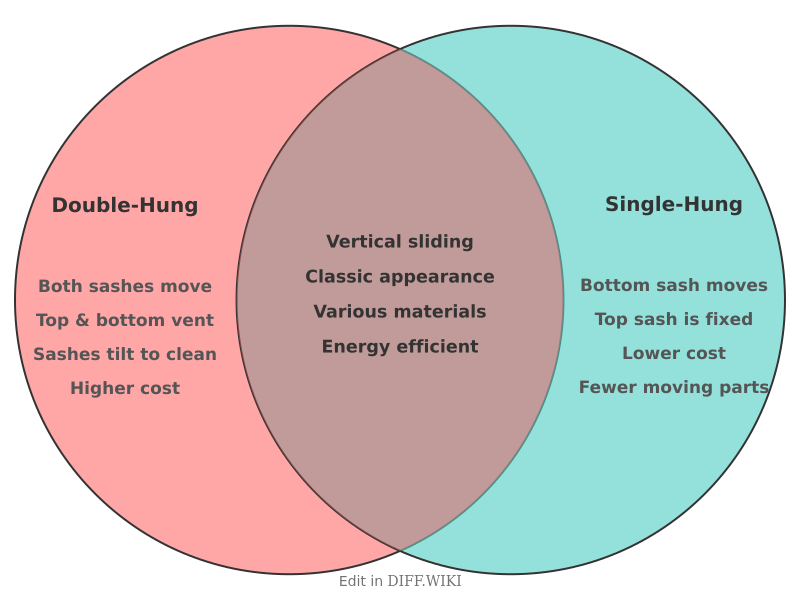
Double-hung and single-hung windows are two of the most common types of windows, particularly in residential buildings.[1] The primary functional difference between them is the operation of their sashes, which are the frames that contain the glass.[2][3] In a single-hung window, the top sash is fixed in place, and only the bottom sash can be moved up and down.[4][5] A double-hung window allows both the upper and lower sashes to be opened and closed independently. This distinction in sash mobility leads to other differences in ventilation, ease of cleaning, and cost.[1]
Comparison Table
| Category | Double-Hung Window | Single-Hung Window |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Both the upper and lower sashes can be moved up and down.[3] | Only the bottom sash is movable; the top sash is fixed.[2][4] |
| Ventilation | Offers more versatile ventilation options. Opening both sashes can create a convection effect, with cool air entering through the bottom and warm air exiting through the top.[3] | Ventilation is limited to the area of the bottom sash opening.[4] |
| Cleaning | Generally easier to clean, especially on upper floors. Most modern double-hung windows have sashes that can tilt inward, allowing both the interior and exterior glass to be cleaned from inside the home. | The exterior of the fixed upper sash can be difficult to clean, often requiring access from the outside.[1] Some modern single-hung windows have a tilting bottom sash for easier cleaning. |
| Cost | Typically more expensive than single-hung windows due to having more moving parts.[3] | Generally the more affordable option. |
| Energy Efficiency | The presence of more moving parts can potentially lead to slightly higher rates of air leakage compared to single-hung windows. However, modern energy-efficient features have made them nearly as efficient as their single-hung counterparts. | With fewer moving parts and a fixed top sash, there is less opportunity for air infiltration, which can make them slightly more energy-efficient.[1] |
| Safety | Can be considered safer for homes with small children, as the top sash can be opened for ventilation while the bottom sash remains closed.[1] | The fixed upper sash can also be seen as a safety feature. |
Additional Considerations
The choice between double-hung and single-hung windows can also be influenced by the architectural style of the home and the specific needs of a room. Single-hung windows are often found in older, historic homes. Due to their simpler operation, they can be a good choice for hard-to-reach areas, such as over a kitchen sink.[2]
Double-hung windows offer greater flexibility for ventilation, which can be beneficial in rooms like bathrooms and kitchens to help manage moisture and odors. The ability to open the top sash is also useful in warmer climates to allow hot air to escape. While historically single-hung windows were considered more energy-efficient, advancements such as low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings, multiple panes of glass, and insulating foam in the frames have significantly improved the performance of both window types. The installation quality also plays a crucial role in the overall energy efficiency of any window.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "thisoldhouse.com". Retrieved December 06, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "pella.com". Retrieved December 06, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "harveywindows.com". Retrieved December 06, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "gvdrenovationsinc.com". Retrieved December 06, 2025.
- ↑ "windowhardwaredirect.com". Retrieved December 06, 2025.