Differences between Electrolysis and Laser Hair Removal
Contents
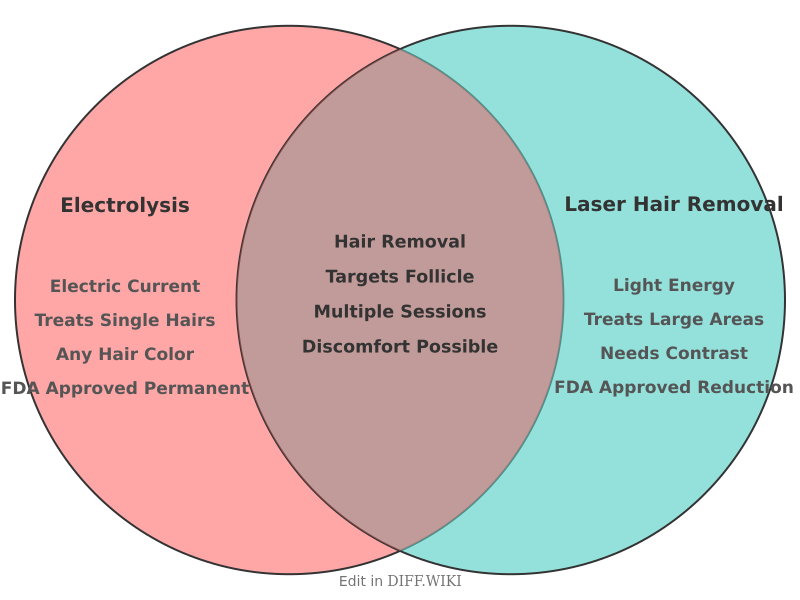
Electrolysis vs. Laser Hair Removal
Electrolysis and laser hair removal are two common methods for long-term hair removal.[1] Electrolysis involves inserting a fine probe into individual hair follicles and applying an electrical current to destroy the hair's growth cells.[2][3] Laser hair removal uses concentrated light beams to target the melanin in hair, which converts to heat and damages the hair follicle.[4][5] While both methods aim to reduce unwanted hair, they differ in their permanence, suitable candidates, and treatment process.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes electrolysis as a method for permanent hair removal. In contrast, the FDA has cleared laser hair removal for "permanent hair reduction," meaning it significantly reduces hair growth over the long term but may not permanently remove all hair.
Comparison Table
| Category | Electrolysis | Laser Hair Removal |
|---|---|---|
| FDA Approval | Approved for permanent hair removal | Cleared for permanent hair reduction |
| Mechanism | An electric current destroys individual hair follicles via a fine probe.[2][3] | Laser light is absorbed by hair pigment, damaging the follicle with heat.[4][5] |
| Suitable Hair and Skin Types | Effective on all hair colors and skin tones.[2] | Most effective on dark, coarse hair and light skin. Not as effective on blonde, red, gray, or white hair. |
| Treatment Areas | Ideal for small, precise areas like eyebrows and the upper lip. | Efficient for larger areas such as the back, legs, and chest. |
| Number of Sessions | Typically requires 15 to 30 sessions for permanent results. | Generally requires 8 to 12 initial treatments. |
| Pain Level | Can cause a stinging or pricking sensation with each follicle treated.[2] | Often described as a warm pinprick or a rubber band snapping against the skin.[4][5] |
| Common Side Effects | Temporary redness, swelling, and minor scabbing are common. | Temporary skin irritation, redness, and pigment changes may occur.[4] |
| Cost | Costs are often based on treatment time, with sessions ranging from 15 to 60 minutes. | Costs are typically priced per session and vary by the size of the treatment area. |
Electrolysis
Electrolysis is a method that has been in use for over a century. A trained electrologist inserts a thin probe into the natural opening of the hair follicle and delivers an electrical current to destroy the hair's growth center.[2] There are three main modalities of electrolysis: galvanic, thermolysis, and a blend of the two.[3]
One of the primary advantages of electrolysis is its versatility. It is effective for all hair colors, including blonde, red, gray, and white, as well as all skin tones.[2] This is because it targets the hair follicle directly, rather than the pigment in the hair. The procedure is often recommended for smaller, more sensitive areas like the face and bikini line. Common side effects are temporary and may include redness, swelling, and slight scabbing.
Laser Hair Removal
Laser hair removal became commercially available in the mid-1990s and works on the principle of selective photothermolysis. This process uses a specific wavelength of light to target the melanin (pigment) in the hair. The light energy converts to heat, which damages the hair follicle and inhibits future growth.[4] Because it relies on pigment, laser hair removal is most effective for individuals with dark hair and light skin, as the contrast allows the laser to target the hair follicle with minimal effect on the surrounding skin.[4]
Advances in laser technology have made the procedure safer and more effective for a wider range of skin tones. However, it remains less effective for hair colors that lack sufficient pigment. The procedure is generally faster than electrolysis for treating large areas like the back or legs because the laser can target multiple follicles at once. Side effects are usually minor and can include temporary redness, swelling, and changes in skin pigmentation.[4]
References
- ↑ "health.com". Retrieved January 15, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "clevelandclinic.org". Retrieved January 15, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "electrology.com". Retrieved January 15, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 "mayoclinic.org". Retrieved January 15, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "webmd.com". Retrieved January 15, 2026.