Differences between Farm-raised Salmon and Wild Salmon
Contents
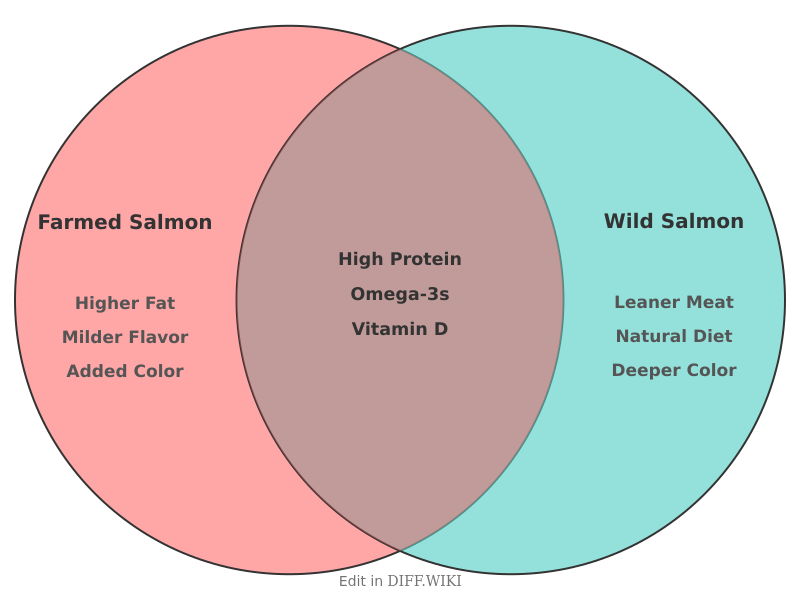
Farm-raised salmon vs. wild salmon
Farm-raised salmon and wild salmon differ considerably in their diet, environment, nutritional composition, and environmental impact. Wild salmon are caught in natural habitats like oceans and rivers, while farm-raised salmon are bred using aquaculture in controlled environments such as ocean net pens or land-based tanks.[1] These differing origins account for the primary distinctions between the two types of fish.
Comparison of attributes
The following table summarizes key differences between farm-raised and wild salmon.
| Attribute | Farm-raised Salmon | Wild Salmon |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Processed feed containing fishmeal, fish oil, and plant proteins like soy or corn.[2] | Natural diet of krill, shrimp, and smaller fish found in their environment.[2] |
| Coloration | Grayish flesh turned pink or red by astaxanthin added to their feed.[3] | Naturally pink or red flesh from consuming astaxanthin in crustaceans like krill.[1] |
| Fat Content | Higher overall fat, including saturated fat and omega-6 fatty acids.[2][4] | Leaner with a lower overall fat content.[4] |
| Omega-3 to Omega-6 Ratio | Lower ratio, with a higher proportion of omega-6 fatty acids.[3][5] | Higher ratio, with a more favorable balance of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids. |
| Contaminants | Can have higher concentrations of contaminants such as PCBs, dioxins, and pesticides.[4] | Generally lower levels of contaminants.[4] |
| Environment | Raised in high-density aquaculture pens in coastal waters or land-based tanks. | Live in natural marine and freshwater ecosystems.[1] |
Diet and coloration
A primary distinction lies in their diet, which directly affects flesh color. Wild salmon consume crustaceans such as krill and shrimp, which are rich in a carotenoid called astaxanthin. This compound gives their flesh its characteristic pink to red hue.[1] Farmed salmon, which eat a processed feed of pellets, would have gray flesh without intervention.[3] To mimic the color of wild salmon, their feed is supplemented with astaxanthin, which can be derived from petrochemicals or natural sources.
Nutritional profile
The nutritional content of salmon varies based on its diet. Farmed salmon generally have a higher total fat content, which can result in a greater amount of omega-3 fatty acids per serving compared to wild salmon.[1] However, the feed for farmed salmon, often containing plant-based oils and proteins, leads to a significantly higher concentration of omega-6 fatty acids.[2] While both types of salmon are sources of omega-3s, wild salmon possess a more balanced omega-3 to omega-6 ratio.[3] Wild salmon is also typically lower in calories and saturated fat and contains more minerals like calcium and iron.[4][5]
Environmental and health considerations
Salmon aquaculture presents several environmental challenges. High-density net pens can lead to the accumulation of fish waste, which pollutes the surrounding marine environment with excess nutrients. Parasites, such as sea lice, can proliferate in these farms and spread to wild fish populations. The use of chemicals and antibiotics to manage disease is another concern.
Studies have shown that farmed salmon can have higher levels of persistent organic pollutants (POPs), including polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and dioxins, which accumulate in the fat of the fish.[4] While contaminant levels in both farmed and wild salmon are often within regulatory safety limits, some research suggests that wild salmon is a safer option, particularly for vulnerable populations.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "northcoastseafoods.com". Retrieved February 02, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "ideafit.com". Retrieved February 02, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "wildalaskancompany.com". Retrieved February 02, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 "clevelandclinic.org". Retrieved February 02, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "healthline.com". Retrieved February 02, 2026.