Differences between Nuvigil and Provigil
Contents
Nuvigil vs. Provigil
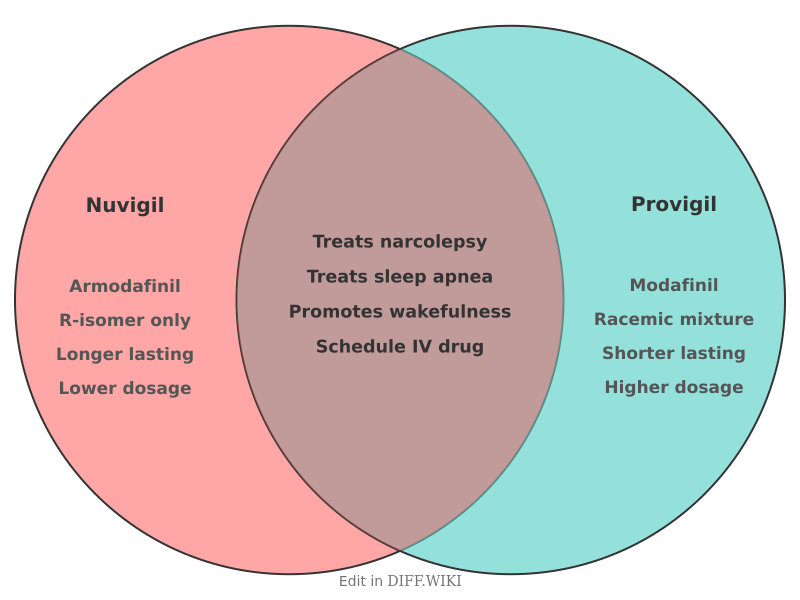
Nuvigil (armodafinil) and Provigil (modafinil) are prescription medications used to improve wakefulness in adults with sleep disorders such as narcolepsy, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and shift work disorder (SWD).[1][2] Both drugs are classified as central nervous system stimulants and are considered Schedule IV controlled substances due to a potential for abuse.[3] While they treat the same conditions and have similar effects, there are key differences in their chemical structure, dosage, and how long they remain active in the body.[3][4]
Provigil was approved by the FDA in 1998, followed by Nuvigil in 2007.[3][5] The primary distinction lies in their active ingredients. Modafinil, the active ingredient in Provigil, is a mixture of two enantiomers—R-modafinil and S-modafinil—which are mirror-image molecules of each other. Nuvigil's active ingredient, armodafinil, consists of only the R-enantiomer. This refinement is intended to provide a more targeted therapeutic effect.
While the exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, both drugs are thought to work by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain that regulate the sleep-wake cycle, including dopamine, norepinephrine, histamine, and orexin.
[3][5]= Comparison Table =
[3]| Half-Life || Approximately 15 hours || Approximately[1][2] 15 hours [1][2]| Duration of Effect || Effects may last longer due to higher plasma concentrations later in the day || Effects[4][5] may be shorter-acting compared to Nuvigil [3]| Typical Dosage || 150 mg to 250 mg once daily || 200[3] mg once daily [4]| Common Side Effects || Headache, nausea, dizziness, insomnia, anxiety, dry mouth || Headache,[3] nausea, nervousness, rhinitis, back pain, diarrhea| Category | Nuvigil (armodafinil) | Provigil (modafinil) |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredient | Armodafinil (R-enantiomer only) | Modafinil (racemic mixture of R- and S-enantiomers) |
| FDA Approval Year | 2007 | 1998[3] |
| Available Strengths | 50 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 250 mg | 100[3] mg, 200 mg |
Chemical Structure and Pharmacokinetics
The main difference between Nuvigil and Provigil is their chemical composition. Provigil contains modafinil, which is a 1:1 mixture of two molecular mirror images, the R-enantiomer and the S-enantiomer. Nuvigil contains only the R-enantiomer, known as armodafinil.
Although both drugs have a similar half-life of about 15 hours, studies have shown that armodafinil (Nuvigil) leads to higher plasma concentrations later in the day compared to modafinil (Provigil). This[2] suggests that Nuvigil's wakefulness-promoting effects may be more sustained throughout the day. Because[4][5] of its longer-lasting effect, a lower dose of Nuvigil (150 mg) may be comparable to a higher dose of Provigil (200 mg).
[4][5]= Approved Uses and Side Effects =
Both Nuvigil and Provigil are FDA-approved to treat excessive sleepiness associated with narcolepsy, obstructive sleep apnea, and shift work disorder. They[3][2] are not cures for these conditions and do not replace the need for adequate sleep.
The[1] side effects of both medications are very similar. The[3] most commonly reported side effect for both is headache. Other[4] shared side effects include nausea, dizziness, anxiety, and trouble sleeping. Provigil[3] has also been associated with side effects not as commonly linked to Nuvigil, such as back pain and rhinitis (runny nose).
[3][2] References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref1 - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref2 - ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref3 - ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref4 - ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedref5
References
Cite error: <ref> tag defined in <references> has group attribute "" which does not appear in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag defined in <references> has group attribute "" which does not appear in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag defined in <references> has group attribute "" which does not appear in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag defined in <references> has group attribute "" which does not appear in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag defined in <references> has group attribute "" which does not appear in prior text.