Differences between SMS and Text
SMS vs. Text
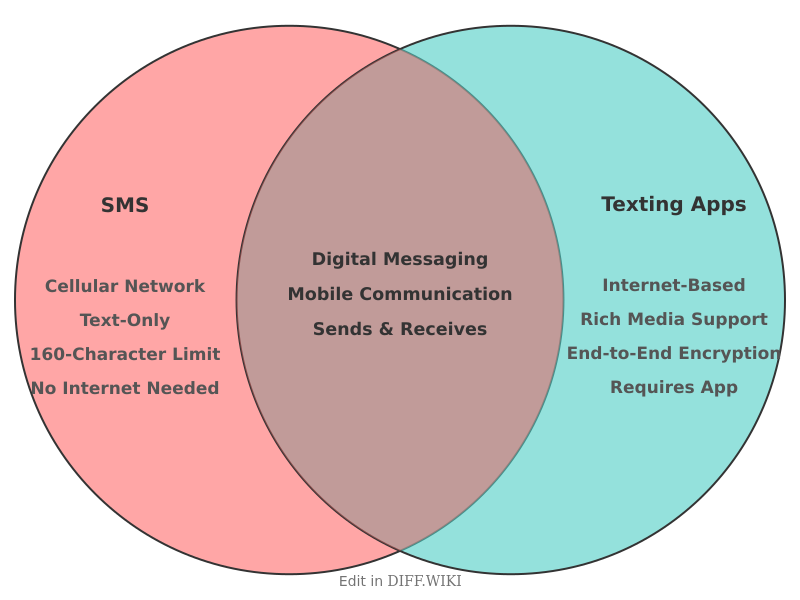
The terms Short Message Service (SMS) and "text" are often used interchangeably, but they do not hold the same meaning. SMS refers to the specific communication protocol used to send and receive short, text-only messages over cellular networks.[1][2] In contrast, "text message" has become a broader term that encompasses various forms of digital messaging, including SMS, as well as messages sent over the internet.[3] While all SMS messages are considered text messages, not every text message is an SMS.[3]
The concept for SMS emerged in the 1980s, and the first message was sent in 1992.[2][4] It was designed as a component of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) standard and is limited to 160 characters.[1][5] This limitation influenced a concise communication style. For messages exceeding this length, the SMS protocol breaks them into multiple segments that are reassembled by the receiving device.
The term "texting" originally referred specifically to sending messages via SMS but has evolved to include messages with multimedia content like images, videos, and audio. These are sent using the Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) protocol, which was built on the same technology as SMS to handle multimedia files.[5] More recently, internet-based messaging applications such as iMessage and WhatsApp have become prevalent. These services use Wi-Fi or mobile data to transmit messages and are not constrained by the limitations of SMS, offering features like longer message lengths, end-to-end encryption, and read receipts.
Comparison Table
| Category | SMS | Modern Text Messaging (e.g., iMessage, WhatsApp) |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying Technology | Cellular network (GSM, CDMA)[1] | Internet (Wi-Fi or mobile data)[3] |
| Content Format | Text-only[5][3] | Text, images, videos, audio, GIFs[5] |
| Message Length | 160-character limit per message[1][5] | Varies by platform, generally much longer |
| Multimedia Support | No, requires MMS for multimedia[5] | Yes, natively supports multimedia content |
| Internet Requirement | Not required | Required |
| Device Compatibility | Universal across all mobile phones | Requires a specific application or operating system |
| Security | Generally unencrypted | Often features end-to-end encryption |
| Cost | Typically part of a mobile carrier plan | Uses mobile data or Wi-Fi, often perceived as free |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved October 14, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "twilio.com". Retrieved October 14, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved October 14, 2025.
- ↑ "textedly.com". Retrieved October 14, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 "crm-messaging.cloud". Retrieved October 14, 2025.