Differences between Server and Workstation
Contents
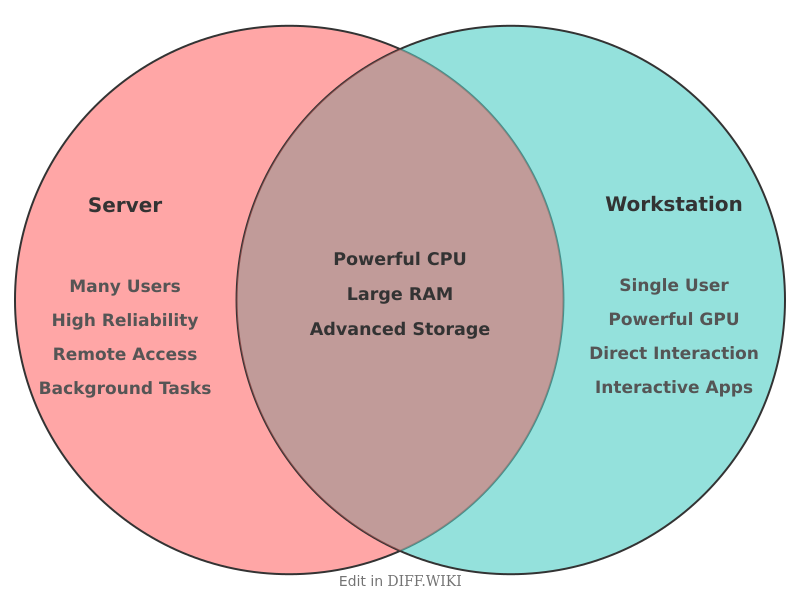
Server vs. Workstation
A server is a computer or software that provides services to other computers, known as clients, over a network.[1][2] Servers are designed to manage network resources and handle requests from multiple clients simultaneously.[3][4] In contrast, a workstation is a high-performance computer designed for a single user to perform technical or scientific tasks.[5] These tasks often require more computational power than a standard personal computer can provide.
The primary distinction between a server and a workstation lies in their intended function. A server is built for continuous, reliable operation to serve multiple users, while a workstation is optimized for performance for an individual user's demanding applications.
Comparison Table
| Category | Server | Workstation |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Provides services and resources to multiple clients over a network.[4] | High-performance computing for a single user's specialized tasks. |
| User Interaction | Typically accessed remotely by many users; may not have a dedicated monitor or keyboard. | Used directly by one person at a time with a dedicated monitor and input devices. |
| Hardware Design | Optimized for 24/7 reliability with redundant components like power supplies and RAID storage.[4] | Optimized for high-speed processing and graphics, with powerful CPUs and GPUs.[4] |
| Operating System | Specialized server OS (e.g., Windows Server, Linux distributions like RHEL, FreeBSD).[1] | Standard desktop OS (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux distributions).[4] |
| Typical Applications | Web hosting, database management, file sharing, email services, application hosting. | 3D rendering, video editing, computer-aided design (CAD), scientific simulations, software development. |
| User Interface | Often managed via a command-line interface (CLI); a graphical user interface (GUI) is optional. | Primarily uses a graphical user interface (GUI) for user interaction. |
Hardware Distinctions
Servers are engineered for uptime and reliability. They often include features such as redundant power supplies and hot-swappable hard drives in a RAID configuration, which allows for component replacement without shutting down the system.[4] The internal components are designed for longevity and continuous operation under heavy load.[3]
Workstations, on the other hand, prioritize performance for specific, resource-intensive tasks. This often translates to having high-end CPUs with many cores, large amounts of RAM, and powerful graphics processing units (GPUs) to accelerate tasks like 3D modeling and video rendering. While workstations use high-quality components, they do not typically have the same level of redundancy as servers.[4]
Operating Systems
The choice of operating system for a server or workstation is dictated by its intended use. Servers commonly run operating systems designed for managing network services and providing stability in multi-user environments.[4] Examples include Windows Server, and various Linux distributions such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Ubuntu Server. These operating systems are optimized for background tasks and may not have a graphical user interface installed by default.[1]
Workstations typically use standard desktop operating systems that are familiar to end-users and support a wide range of professional software applications.[4] Common workstation operating systems include Microsoft Windows, macOS, and various distributions of Linux. These operating systems provide a graphical user interface and are designed for interactive use by a single person.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 28, 2026.
- ↑ "geeksforgeeks.org". Retrieved January 28, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "reddit.com". Retrieved January 28, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 "oreateai.com". Retrieved January 28, 2026.
- ↑ "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 28, 2026.