Differences between Skim Milk and Whole Milk
Contents
Comparison Article
I have gathered substantial information on the nutritional differences, processing methods, culinary applications, and health aspects of skim and whole milk. I have details on fat content, calorie counts, vitamin and mineral levels, and the processes of centrifugation, fortification, and homogenization. The search results also provide insights into how the fat content affects taste, texture, and use in cooking and baking. I believe I have sufficient information to create the Wikipedia-formatted article as requested, adhering to the specified guidelines. Therefore, I will now proceed to write the article. I am ready to write the article. .
Skim Milk vs. Whole Milk
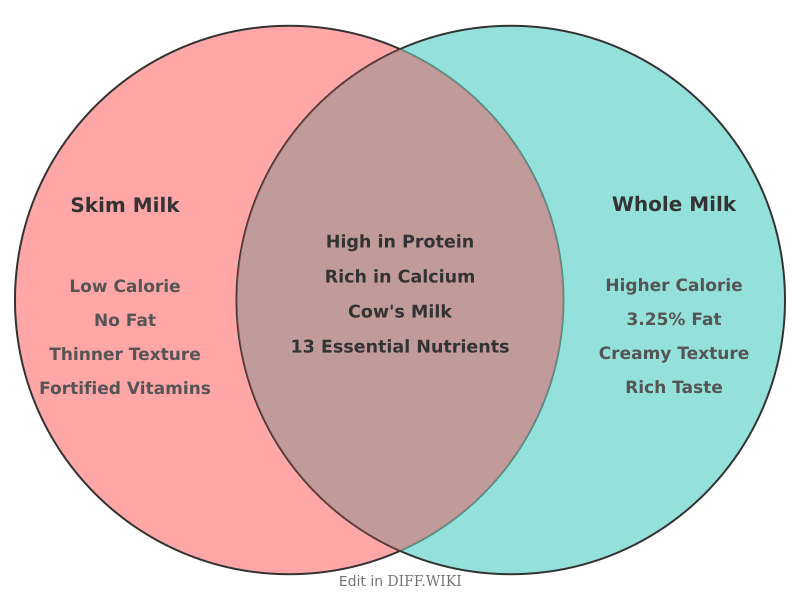
Skim milk and whole milk are two common types of cow's milk that differ primarily in their fat content.[1][2] This variation in fat composition leads to differences in nutritional value, taste, texture, and culinary applications.[3][4] The choice between skim and whole milk often depends on individual dietary needs, taste preferences, and health goals.[5]
The processing of skim milk involves the removal of almost all milk fat. This is typically achieved through a process called centrifugation, where whole milk is spun at high speeds to separate the cream (fat) from the milk. Conversely, whole milk retains all of its natural milk fat, which is approximately 3.25% to 3.5% by weight.[1] Both types of milk are usually pasteurized to kill harmful bacteria and homogenized to prevent the cream from separating and rising to the top.
Because the fat-soluble vitamins A and D are removed along with the cream, skim milk in many regions is fortified with these nutrients to restore its nutritional value. Whole milk naturally contains vitamin A, and both types are often fortified with vitamin D.
Comparison Table
[5][2]| Protein (per cup) || About 8 grams || About 8 grams [4]| Culinary Uses || Suitable for smoothies and oatmeal where other ingredients provide richness. || Preferred[4] for richer sauces, baked goods, and creamier coffee beverages.| Category | Skim Milk | Whole Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | Less than 0.5%[1] | Approximately 3.25%–3.5% |
| Calories (per cup) | Approximately 80–85 | Approximately[5] 150 |
| Calcium | Contains slightly more calcium than whole milk. | A[1] good source of calcium. |
| Vitamins | Fortified with vitamins A and D, as the natural vitamins are lost with fat removal. | Naturally contains vitamin A; often fortified with vitamin D. |
| Taste and Texture | Watery consistency and less creamy taste. | Creamy texture and richer flavor. |
Nutritional Considerations
The primary nutritional difference between skim and whole milk lies in their calorie and fat content. A cup of whole milk contains significantly more calories and saturated fat than a cup of skim milk. For[5] individuals managing their calorie or saturated fat intake, skim milk can be a suitable option. However, recent research suggests that the saturated fat from dairy products may not have the same negative cardiovascular effects as saturated fat from other sources.
Both[5] skim and whole milk are excellent sources of protein and calcium, with skim milk containing a slightly higher concentration of calcium. They[1] also provide other essential nutrients such as phosphorus, potassium, and B vitamins.
Culinary Applications
The fat content of milk plays a significant role in its performance in cooking and baking. The richness of whole milk contributes to a fuller flavor and creamier texture in dishes like sauces, soups, and baked goods. The[4] fat in whole milk also helps to create a tender crumb in cakes and muffins.
Skim milk, due to its lower fat content, has a thinner consistency and a less rich flavor. While it can be used in many of the same applications as whole milk, the resulting dish will be lighter. It is often used in preparations where other ingredients contribute richness and flavor, such as smoothies. In coffee,[4] whole milk produces a creamier, more flavorful beverage, while skim milk creates a lighter drink with more foam.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "healthline.com". Retrieved January 23, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "gonnaneedmilk.com". Retrieved January 23, 2026.
- ↑ "fitnesssimplified.org". Retrieved January 23, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 "organicvalley.coop". Retrieved January 23, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "foodnetwork.com". Retrieved January 23, 2026.