Difference Between DDR3 and DDR4
When it comes to short term memory, DDR3 and DDR4 are two options. While the number of DDR4 options are increasing in the market, many people still prefer to use DDR3. Here are the distinctions between DDR3 and DDR4.
DDR3[edit]
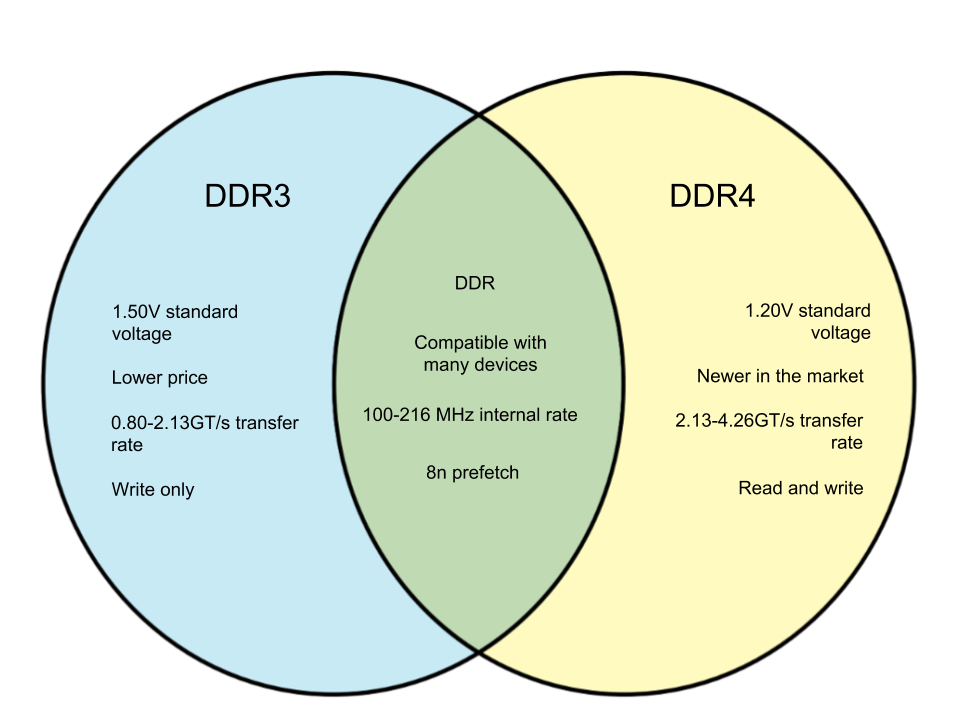
The DDR3 runs at 1.5 volts with specifications that start at 800 MT/s. It has a bandwidth of 400-1066 MHz for bus clock and an internal rate of 100-266 MHz. DDR3s cost less than DDR4 and are still compatible with many devices at present. They can possess a memory density of 512 Mb to 8Gb and a write-only mode register.
DDR4[edit]
The DDR4 reduces the voltage consumption at 1.2 volts. This may not be significant for home PCs, but it can make a big difference for establishments that run hundreds of systems and thousands of DD4s. The speed also increases to 2,133 MHz and may go even higher, resulting in increased bandwidth. There is a higher transfer rate for DDR4 modules at reduced voltages, reducing the risk of damaging the RAM on overclocking tests.
| DDR3 | DDR4 | |
|---|---|---|
| Low voltage | 1.35V | 1.05V |
| Standard Voltage | 1.50V | 1.20V |
| Performance Voltage | 1.65V | 61.35V |
| Bus Clock | 400-1066MHz | 1066-2133MHz |
| Internal Rate | 100-266 MHz | 100-266 MHz |
| Transfer Rate | 0.80-2.13GT/s | 2.13-4.26GT/s |
| Mode Register | Write | Read/Write |
| Boundary Scan | No | Yes |