Difference between Overweight and Obesity
Excessive weight is one of the factors that can affect health, and poses possible complications such as diabetes and heart problems. Obesity is one of the leading concerns in health, especially with the presence of unhealthy diets like processed food and junk food. In this article, we will discuss what it means to be overweight as opposed to being obese.
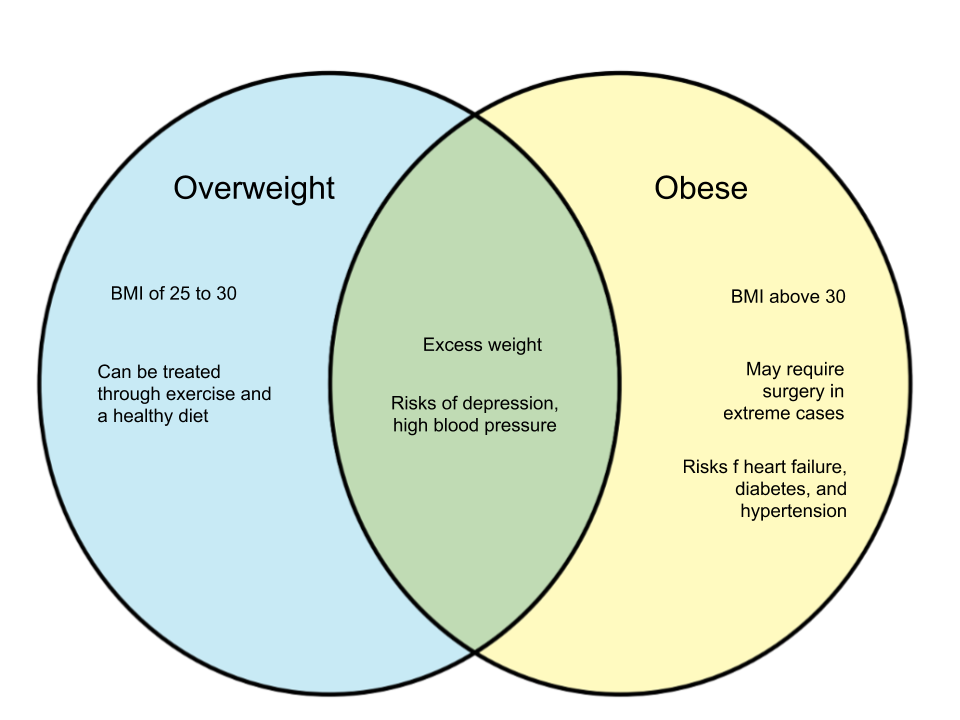
The term “overweight” is often used to refer to someone whose weight is 10 to 20 percent higher than normal. The normal weight of an individual can be derived using a standard height/weight chart or the body mass index (BMI). The standard BMI for a person is 25 or 30, and when one has exceeded that, they can be considered overweight. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines someone as overweight when they possess a BMI of 25 to 29.9.
On the other hand, when one has reached a BMI of 30 or higher, they are classified as obese. When a person reaches 50 to 100 percent their normal height, the term used is “morbid obesity”. Obesity is considered a serious health risk, especially in America. Obesity implicates risks such as diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension.
BMI is not the only means to determine if one is overweight or obese. The system itself has its own faults, like being unable to take into account if an individual is muscular or if their bones and other variables play a role in their weight. Calipers, bioelectrical impedance, DEXA, and hydrostatic body fat tests are some of the more accurate means to measure body fat and determine the presence of obesity.
In summary, both terms have the same implications of weight in excess than one’s normal state. The difference lies in the scale of excess and in turn the severity of effects posed on physical and mental health.
| Overweight | Obesity | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Someone whose weight is above normal, depending on various variables like sex, age, and height. | Someone with the condition where they have accumulated excessive body fat that it poses health concerns. |
| BMI | 10 to 20 percent higher than normal; usually with a BMI of 25 to 30. | 20 percent or higher than normal, or a BMI of 30 or above. |
| Causes | Excessive eating, bad dietary and sleep habits, lack of exercise. | Excessive eating, bad dietary and sleep habits, lack of exercise, genetics, hormonal imbalance, stress. |
| Risks | High blood pressure, depression, low self-esteem | High blood pressure, depression, low self-esteem, coronary heart disease, diabetes, hypertension. |
| Treatment | Exercise and a healthy diet. | Exercise, a healthy diet, surgery in severe cases. |