Differences between ABS and PVC
Contents
ABS vs. PVC[edit]
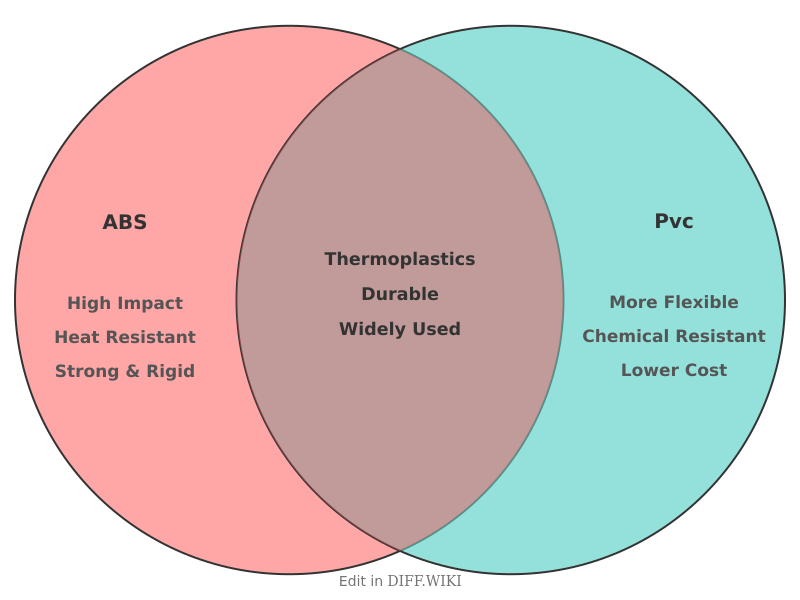
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) are two common thermoplastic polymers widely used in various applications, particularly in piping and construction materials.[1][2][3] Both materials offer durability and resistance to corrosion, serving as lightweight and cost-effective alternatives to traditional materials like metal.[4][5] While they share some similarities, their distinct chemical compositions and physical properties make them suitable for different purposes.[1]
Comparison Table[edit]
[1][4]| Sunlight Exposure || Can be damaged by prolonged exposure to direct sunlight. || Generally[4] more resistant to UV radiation.| Category | ABS | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | A terpolymer made from acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene.[1] | A vinyl polymer derived from vinyl chloride.[1] |
| Appearance | Typically black in color. | Generally white or off-white. |
| Impact Resistance | Higher impact strength and toughness, especially at low temperatures. | More brittle than ABS and can be prone to cracking under extreme force. |
| Flexibility | More rigid and strong. | More flexible than ABS, which can be an advantage in tight installations. |
| Temperature Tolerance | [1]| Can handle hot water up to 140°F (60°C) but can become brittle in freezing temperatures. | |
| Installation | Joined using a one-step solvent cement process. | Requires a two-step process involving a primer and then solvent cement. |
| Cost | Can be slightly more expensive than PVC. | Generally less expensive, making it a cost-effective option for large projects. |
| Common Applications | Drain, waste, and vent (DWV) pipes, automotive parts, electronic housings, and toys like LEGO bricks. | Water[1] supply lines, window frames, siding, electrical cable insulation, and flooring. |
Chemical Composition and Safety[edit]
A notable difference in the chemical makeup of the two plastics is the presence of Bisphenol A (BPA) in ABS. BPA is used to harden the plastic, and while regulatory bodies have deemed it safe in small amounts, its presence has led some to prefer PVC for applications involving drinking water. PVC[4] is free of BPA.
Durability and Performance[edit]
ABS is known for its strength and higher impact resistance, making it less likely to crack or break during installation or under stress. It also performs well in a wider range of temperatures, from very cold to hot, without deforming. PVC, while also durable, is more brittle than ABS. However, its flexibility can be an advantage in plumbing applications that require navigating tight spaces. PVC is also noted for being better at muffling the sound of flowing water compared to ABS.
Installation and Cost[edit]
The installation process for the two materials differs. ABS pipes can be joined with a special cement in a single step. PVC pipe installation is a two-step process that requires the application of a primer before the cement. In terms of cost, PVC is often the more affordable option. While ABS material costs may be slightly higher, the simpler installation process can sometimes offset the overall project cost.
Recycling and Environmental Considerations[edit]
Both ABS and PVC are recyclable, though the processes can be intensive. Recycling these plastics helps to reduce the need for virgin material production, which in turn conserves resources and reduces energy consumption. The recycling process for both materials typically involves sorting, cleaning, shredding, and then melting the plastic to be reformed into new products.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "plumbing-united.com". Retrieved December 25, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "plasticseurope.org". Retrieved December 25, 2025.
- ↑ "specialchem.com". Retrieved December 25, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "monkeywrenchplumbers.com". Retrieved December 25, 2025.
- ↑ "coextrudedplastics.com". Retrieved December 25, 2025.