Differences between AK-47 and AK-74
Contents
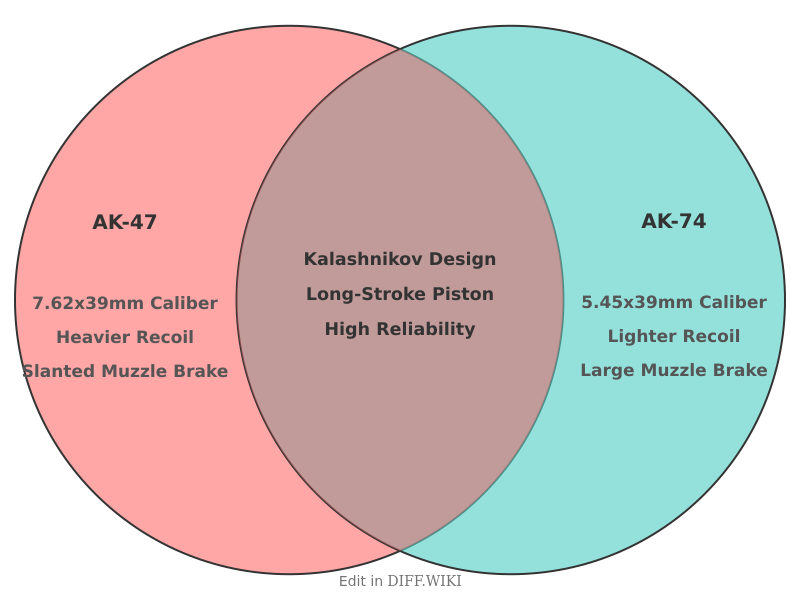
AK-47 vs. AK-74[edit]
The AK-47 and AK-74 are two related but distinct assault rifles developed in the Soviet Union. The AK-47, officially adopted in 1949, was chambered for the 7.62x39mm cartridge. In the 1970s, following a global trend towards smaller, higher-velocity military cartridges, the Soviet Union developed the 5.45x39mm round and a new rifle to fire it, the AK-74.[1][2][3] The AK-74 was designed as a successor to the AKM (a modernized, stamped-receiver version of the AK-47) and officially entered service in 1974.[4][2] While both rifles share the same basic Kalashnikov operating system and have many interchangeable parts, they have key differences in caliber, external features, and performance.[1][5]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | AK-47 (AKM) | AK-74 |
|---|---|---|
| Cartridge | 7.62x39mm | 5.45x39mm[1] |
| Year Introduced | 1949 (AK-47), 1959 (AKM) | 1974[2] |
| Muzzle Device | Slanted compensator (AKM) or thread protector | Large, multi-chamber muzzle brake |
| Muzzle Velocity | ~730 m/s (2,395 ft/s) | ~890 m/s (2,920 ft/s) |
| Magazine | Steel, pronounced curve | Polymer/Bakelite, less pronounced curve |
| Furniture Material | Primarily wood | Laminated wood, later polymer ("plum" or black)[2] |
| Gas Block | 45-degree angle | 90-degree angle |
| Unloaded Weight | ~4.3 kg (9.5 lbs) | ~3.07 kg (6.8 lbs)[2] |
Cartridge and Ballistics[edit]
The most significant difference is the ammunition. The AK-47's 7.62x39mm is a heavier, larger-diameter bullet that delivers substantial energy at close ranges. The AK-74's 5.45x39mm cartridge fires a lighter projectile at a much higher velocity.[1] This results in a flatter trajectory, a longer effective range, and significantly reduced recoil compared to the 7.62mm round.[5] The lighter weight of the 5.45x39mm ammunition also allows a soldier to carry more rounds for the same overall weight.[5]
External Features[edit]
Several visual distinctions make the rifles easy to identify. The most prominent is the muzzle device. The AK-74 is equipped with a large, complex muzzle brake designed to counteract recoil and muzzle rise. The AKM, a common variant of the AK-47, typically features a smaller, slanted compensator.
Magazines also differ. The 7.62x39mm cartridge's significant case taper requires a deeply curved "banana" magazine, usually made of steel. The 5.45x39mm cartridge has less taper, resulting in a straighter magazine, which was commonly made from reddish-brown Bakelite or later, polymer composites. Additionally, the furniture on early AK-74s was laminated wood, but this was later replaced with polymer, often in a distinctive "plum" color before changing to black on the updated AK-74M model.[2][3]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "sdi.edu". Retrieved November 25, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved November 25, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "americanrifleman.org". Retrieved November 25, 2025.
- ↑ "kalashnikovgroup.ru". Retrieved November 25, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "wideners.com". Retrieved November 25, 2025.