Differences between Advil and Aleve
Advil vs. Aleve[edit]
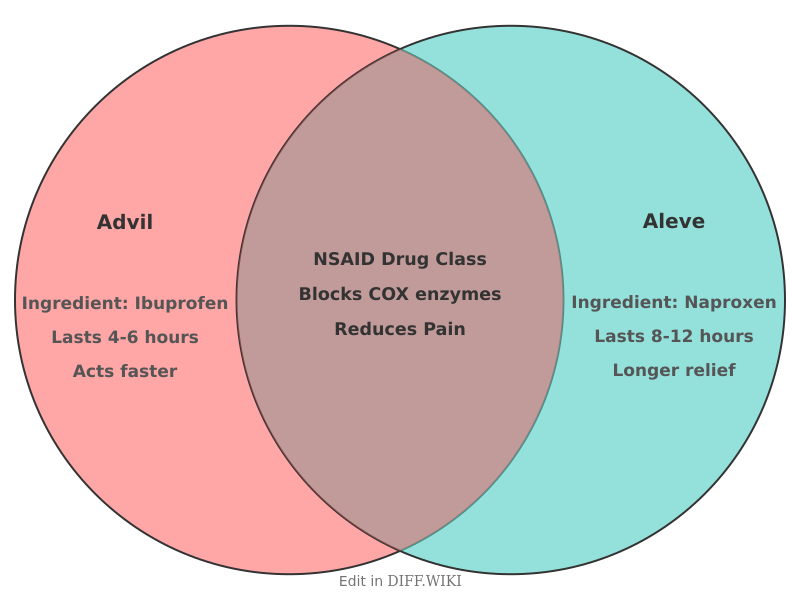
Advil and Aleve are over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) used to treat pain, inflammation, and fever.[1][2] While both medications work by blocking the production of prostaglandins, chemicals that contribute to pain and inflammation, they have key differences in their active ingredients, duration of action, and dosing schedules.[3][4][5] Advil's active ingredient is ibuprofen, while Aleve's is naproxen sodium.[1]
One of the primary distinctions between the two is how long they last. Aleve has a longer duration of action, with pain relief typically lasting up to 12 hours.[1][2] Advil is shorter-acting, requiring doses every four to six hours.[1] This difference is due to the half-life of the active ingredients; naproxen has a half-life of 12 to 17 hours, compared to ibuprofen's 1.5 to 2 hours.[2] Consequently, Aleve may be more suitable for chronic conditions, while Advil is often used for acute pain.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Advil | Aleve |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredient | Ibuprofen | Naproxen Sodium[1] |
| Drug Class | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) |
| How it Works | Blocks COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes to reduce prostaglandins[5] | Blocks COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes to reduce prostaglandins |
| Duration of Action | 4 to 6 hours[1] | 8 to 12 hours[1] |
| Time to Take Effect | Works more quickly than Aleve | Takes longer to work than Advil |
| Standard Adult Dose | 1 to 2 tablets (200-400 mg) every 4 to 6 hours | 1 tablet (220 mg) every 8 to 12 hours |
| Maximum Daily Dose (OTC) | 6 tablets (1200 mg) | 3 tablets (660 mg) |
| Use in Children | Approved for children over 6 months of age (dosage varies by weight) | Not recommended for children under 12 unless directed by a doctor[1] |
Side Effects and Risks[edit]
Both Advil and Aleve share similar potential side effects, which are common to NSAIDs. These can include stomach pain, heartburn, nausea, and gas. Because NSAIDs can interfere with the protective lining of the stomach, more serious gastrointestinal issues like ulcers and bleeding are possible, with the risk increasing with longer use. Aleve may be more likely to cause gastrointestinal side effects due to its longer duration of action.
All NSAIDs, including ibuprofen and naproxen, carry a warning about an increased risk of heart attack and stroke. These medications can also affect kidney function and increase blood pressure. Individuals with a history of heart disease, kidney problems, or stomach ulcers should consult a healthcare provider before using either medication. It is important not to take Advil and Aleve together, as this increases the risk of adverse effects without providing additional benefit.[2]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "verywellhealth.com". Retrieved January 09, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "medicalnewstoday.com". Retrieved January 09, 2026.
- ↑ "walshmedicalmedia.com". Retrieved January 09, 2026.
- ↑ "betterhealth.vic.gov.au". Retrieved January 09, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 09, 2026.