Differences between Almond Milk and Soy Milk
Contents
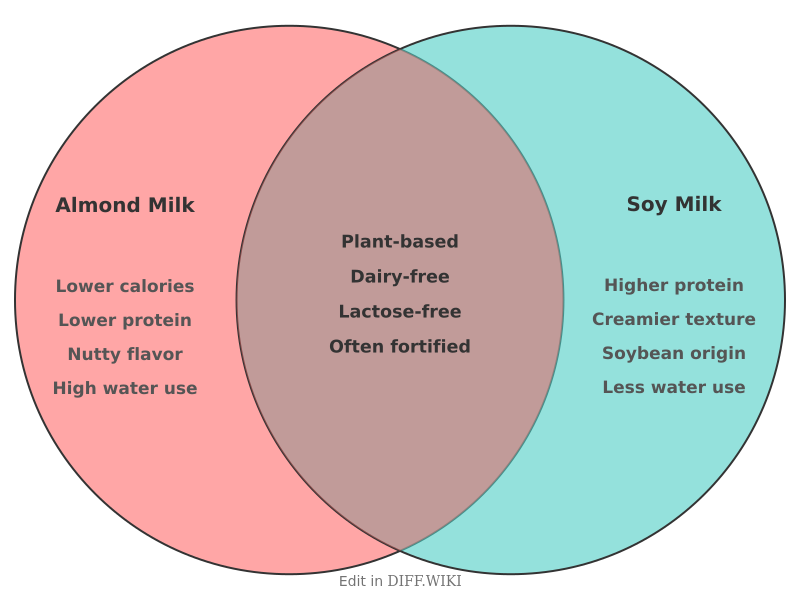
Almond Milk vs. Soy Milk[edit]
Almond milk and soy milk are two of the most widely available plant-based alternatives to dairy milk.[1] Almond milk is produced by blending almonds with water and filtering the solids, while soy milk is made from soaked, ground, and boiled soybeans.[2] Both are naturally lactose-free and low in cholesterol.[1] Their nutritional content, culinary uses, and environmental impacts differ.
Many commercially available almond and soy milks are fortified with calcium and vitamin D to better replicate the nutritional profile of cow's milk.[3][1] Consumers may choose unsweetened versions to avoid added sugars.[4]
Comparison Table[edit]
[2]| Texture || Thinner, more watery || Thicker, creamier| Category | Almond Milk | Soy Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Ingredient | Ground almonds and water[4] | Ground soybeans and water[4] |
| Protein (per cup, unsweetened) | ~1 gram[3][5] | 6–9 grams |
| Calories (per cup, unsweetened) | ~30–50 | [3]~91 |
| Taste | Mild, nutty, slightly sweet | Creamier,[2] with a more pronounced bean-like flavor |
| Common Allergens | Tree nuts | Soy |
| Water Usage (per 200ml) | ~74 liters | ~5.6 liters |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions (per 200ml) | ~0.14 kg | ~0.20 kg |
Nutritional Profile[edit]
Soy milk is significantly higher in protein than almond milk, offering an amount comparable to cow's milk. This makes it a more suitable option for individuals seeking to increase their protein intake, including for muscle growth or recovery. Almond milk is lower in calories, which may be preferable for those monitoring their caloric intake.
Soy[5] milk contains polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats and isoflavones, which are antioxidants. Almond[4] milk is a source of monounsaturated fats and vitamin E.
[4][3]= Culinary Uses =[edit]
The milder, nutty flavor of almond milk makes it versatile for uses in smoothies, cereals, and coffee without significantly altering the taste. However, due to its lower fat and protein content, it does not froth as well as soy milk and its thin consistency can affect the texture of baked goods.
Soy milk's thicker and creamier texture more closely resembles dairy milk, making it a better substitute in baking and for creating foam in coffee drinks. Its[2] more distinct flavor is noticeable and can complement savory dishes, and it serves as a base for products like tofu and non-dairy cheese.
[2]= Allergies =[edit]
Almond milk is not safe for individuals with tree nut allergies, as even small amounts of almond protein can trigger allergic reactions. Soy is also one of the major food allergens. Allergic reactions to soy are typically mild but can be severe. People with soy allergies should avoid soy milk and other soy-based products.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Both plant-based milks have a lower environmental impact than cow's milk in terms of land use and greenhouse gas emissions. Almond cultivation is water-intensive, requiring significantly more water than soy. A large[4] portion of the world's almonds are grown in California, a region that has faced drought conditions. Soy[4] milk production uses less water. However, soybean cultivation has been linked to deforestation in some regions, although the majority of soy is grown for animal feed rather than for direct human consumption.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "medicalnewstoday.com". Retrieved December 22, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "youtube.com". Retrieved December 22, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "nd.edu". Retrieved December 22, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 "kimdenkhaus.com". Retrieved December 22, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "lexhealth.com". Retrieved December 22, 2025.