Differences between Alprazolam and Lorazepam
Contents
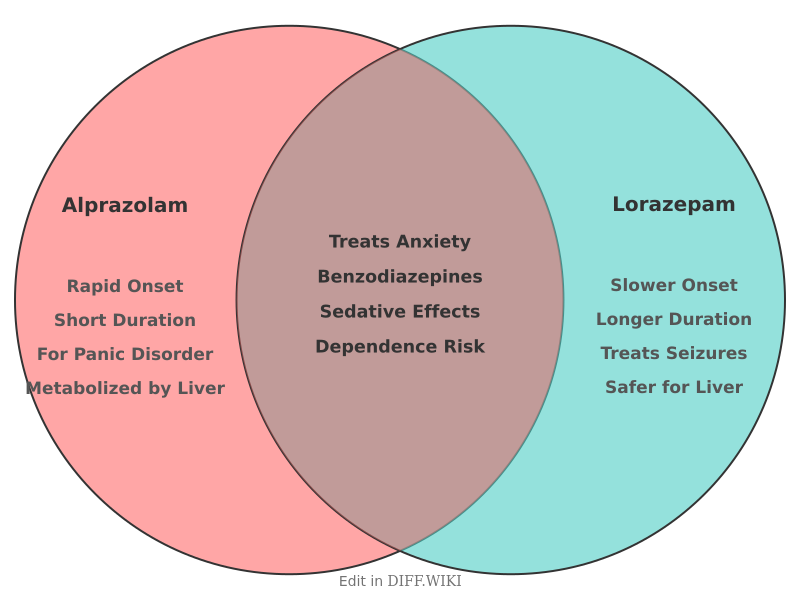
Differences between Alprazolam and Lorazepam[edit]
Alprazolam and lorazepam are medications belonging to the benzodiazepine class, which act on the central nervous system to produce a calming effect.[1] Both are prescribed for the management of anxiety disorders, but they possess distinct pharmacokinetic and clinical profiles that influence their use in different medical scenarios.[2][3] Key differences include their metabolism, elimination half-life, and specific approved uses.[4]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Feature | Alprazolam | Lorazepam |
|---|---|---|
| Brand Names | Xanax, Niravam[5] | Ativan, Loreev XR |
| Onset of Action (Oral) | Intermediate (peak plasma levels in 1-2 hours) | Intermediate (peak plasma levels in 2 hours) |
| Elimination Half-Life | 11.2 hours in healthy adults (range 6.3-26.9 hours) | 10-20 hours |
| Metabolism | Hepatic, primarily by the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) enzyme system | Hepatic, via glucuronide conjugation |
| Active Metabolites | Yes (α-hydroxyalprazolam and 4-hydroxyalprazolam), but they contribute little to the overall effect | No clinically active metabolites |
| Primary FDA-Approved Uses | Anxiety disorders, panic disorder (with or without agoraphobia) | Anxiety disorders, insomnia due to anxiety, status epilepticus, preoperative sedation |
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
The primary pharmacokinetic difference between alprazolam and lorazepam lies in their metabolic pathways. Alprazolam[4] is extensively metabolized in the liver by the CYP3A4 enzyme. This means its clearance can be affected by other drugs that inhibit or induce this enzyme, leading to potential drug interactions. In[5] contrast, lorazepam undergoes metabolism through glucuronidation, a process that is less susceptible to drug-drug interactions. This metabolic pathway also makes lorazepam a potentially safer option for patients with impaired liver function.
While both drugs have an intermediate onset of action after oral administration, their elimination half-lives differ slightly. Alprazolam's half-life is approximately 11.2 hours in healthy adults, though this can be prolonged in the elderly and in individuals with obesity or alcoholic liver disease. Lorazepam has a half-life ranging from 10 to 20 hours. This longer duration can allow for less frequent dosing but may lead to accumulation, especially in patients with renal impairment.
Clinical Applications[edit]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved alprazolam for the treatment of anxiety disorders and panic disorder. It[5] is particularly noted for its efficacy in managing panic attacks. [2][3] Lorazepam has a broader range of FDA-approved indications, including anxiety, insomnia caused by anxiety, status epilepticus, and as a preanesthetic medication to provide sedation and amnesia. Its availability in an injectable formulation allows for rapid administration in acute settings, such as for the control of active seizures or severe agitation. Off-label uses for lorazepam include treatment for alcohol withdrawal and chemotherapy-induced nausea.
References[edit]
- ↑ "boulevarddentalgroup.com". Retrieved February 10, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "nih.gov". Retrieved February 10, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "oreateai.com". Retrieved February 10, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "droracle.ai". Retrieved February 10, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved February 10, 2026.