Differences between Analog and Digital
Contents
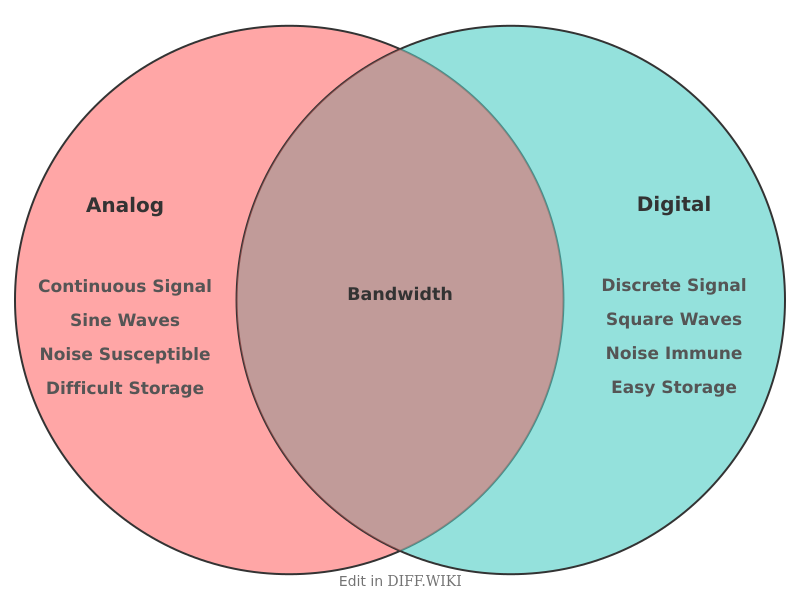
Analog vs. Digital Signals[edit]
Analog and digital signals are two methods of transmitting information.[1] The primary difference between the two is that an analog signal is continuous, while a digital signal is discrete.[1][2] Analog signals represent information using a continuous range of values, whereas digital signals use a finite set of discrete values, typically represented as a sequence of 0s and 1s (binary).[3][4]
An analog signal can be any continuous wave that varies in amplitude or frequency to represent information.[5] Natural phenomena such as sound, light, and temperature are inherently analog, and devices like microphones and traditional thermometers transduce these physical variables into analog electrical signals.[4]
In contrast, a digital signal represents information as a sequence of discrete values.[5] This is achieved by sampling an analog waveform at specific intervals and quantizing each sample to a specific numerical value. Most modern electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and other data communication technologies, utilize digital signals.[2]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Analog Signal | Digital Signal |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Continuous wave with an infinite number of possible values within its range. | Discrete wave with a finite number of distinct values. |
| Representation | Represented by sine waves, conveying information through variations in amplitude, frequency, or phase.[2] | Represented by square waves, conveying information in binary format (0s and 1s).[2] |
| Noise Immunity | More susceptible to noise and distortion, which can degrade signal quality.[4] | Less affected by noise; error detection and correction techniques can be employed for more reliable transmission. |
| Bandwidth | Generally consumes less bandwidth for the same information content.[1] | Requires higher bandwidth for transmission compared to analog.[1] |
| Fidelity | Can provide a more accurate and detailed representation of the original information. | Conversion from analog to digital can introduce quantization errors, though higher precision can be achieved by using more binary digits.[4] |
| Storage & Copying | Storage is difficult, and each copy degrades in quality (generation loss). | Can be easily stored on various media and copied without any loss of quality.[3] |
| Flexibility & Processing | Signal processing is less flexible.[2] | Highly flexible; signals can be easily manipulated, compressed, and encrypted with software.[1][3] |
| Examples | Human voice, audio tapes, traditional thermometers, older television broadcasts.[2][5] | Computers, CDs, DVDs, smartphones, modern television broadcasts.[2] |
Characteristics of Analog Signals[edit]
Analog signals are defined by their continuity, meaning they can represent any value within a given range.[2] This allows for a very high density of information and a nuanced representation of physical phenomena. For example, the voltage from a microphone varies in direct analogy to the pressure of sound waves.[4] However, this continuous nature also makes analog signals vulnerable to noise and interference. Any unwanted variation in the signal can be difficult to distinguish from the original information, and this noise accumulates with each transmission or copy, leading to irreversible degradation known as generation loss.
Characteristics of Digital Signals[edit]
Digital signals encode information into a discrete set of values, making them inherently more robust against noise. Small fluctuations in the signal caused by interference are less likely to be misinterpreted, as the receiving device only needs to distinguish between a finite number of states (e.g., high or low voltage). This allows for error detection and correction codes to be implemented, ensuring the integrity of the data over long distances and through multiple copies.[3] The digital format also allows for greater flexibility in processing, including data compression and encryption.[1] However, the process of converting an analog signal to a digital one, known as sampling and quantization, can introduce small inaccuracies called quantization error.[4] Additionally, digital transmission typically requires more bandwidth than analog transmission for the same information.[1]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "turito.com". Retrieved October 28, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 "khanacademy.org". Retrieved October 28, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "geeksforgeeks.org". Retrieved October 28, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved October 28, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "igitsarang.ac.in". Retrieved October 28, 2025.