Differences between Bed Bugs and Fleas
Contents
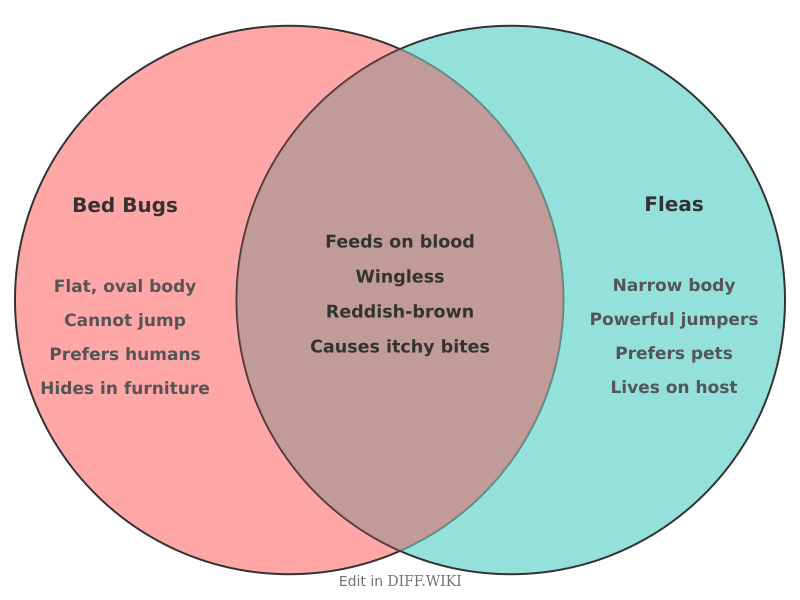
Bed Bugs vs. Fleas[edit]
Bed bugs and fleas are both small, parasitic insects that feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals.[1][2] While both can cause uncomfortable bites and infestations in homes, they belong to different scientific orders and have distinct characteristics in terms of appearance, behavior, and the health risks they pose.[1][2] Bed bugs are classified under the family Cimicidae, while fleas belong to the order Siphonaptera.[2] Understanding these differences is key to proper identification and effective pest control.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Bed Bugs | Fleas |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Flat, oval-shaped body, reddish-brown, and about 1-7 mm in length.[3][4] | Long, narrow body that is compressed from side to side, dark reddish-brown, and smaller at 1.5-3.3 mm long.[3][5] |
| Mobility | Crawl but cannot fly or jump.[3] | Possess long legs and can jump significant distances.[3] |
| Preferred Host | Primarily humans. | Primarily pets like cats and dogs, but will bite humans. |
| Habitat | Hide in cracks and crevices near sleeping areas, such as mattresses, bed frames, and furniture.[3][5] | Live on their animal hosts and in pet bedding, carpets, and upholstery.[5] |
| Bite Appearance | Raised, flat red welts, often appearing in a line or cluster.[3][5] | Small, itchy red spots, sometimes with a dark red center, appearing in random clusters.[3] |
| Bite Reaction Time | Itchiness may be delayed, appearing hours or even days after the bite.[3] | Bites are typically felt and become itchy almost immediately. |
| Disease Transmission | Not known to transmit infectious diseases to humans. | Can transmit diseases such as murine typhus, plague, and cat-scratch fever.[3] |
| Life Cycle | Undergo incomplete metamorphosis (egg, nymph, adult).[1] | Undergo complete metamorphosis (egg, larva, pupa, adult). |
Health Implications[edit]
The health effects of bed bug and flea bites differ significantly. Bed bug bites can cause a range of skin reactions, from small red marks to larger welts and blisters. While they are not known to spread pathogens, their bites can lead to secondary skin infections from scratching, such as impetigo. Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to the bites. Additionally, infestations can cause psychological distress, including anxiety and insomnia.
Flea bites also cause itchy, red bumps. A more significant health concern with fleas is their ability to act as vectors for various diseases. Fleas can transmit bacterial diseases to humans, including murine typhus and, historically, the bubonic plague. They can also transmit bartonellosis (cat-scratch disease) and parasites like tapeworms.
Signs of Infestation[edit]
Identifying the correct pest is crucial for eradication. Signs of a bed bug infestation include visible live bugs, rust-colored spots from their excrement on mattresses and furniture, and shed skins.[5] Flea infestations are often indicated by pets constantly scratching, the presence of "flea dirt" (flea feces) on a pet's fur or bedding, and seeing the fleas themselves jumping.[5]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "rentokil.com". Retrieved December 09, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "doctorguideonline.com". Retrieved December 09, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 "terminix.com". Retrieved December 09, 2025.
- ↑ "bettertermite.com". Retrieved December 09, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 "bettercallbugtech.com". Retrieved December 09, 2025.