Differences between Caucus and Primary
Contents
Comparison Article[edit]
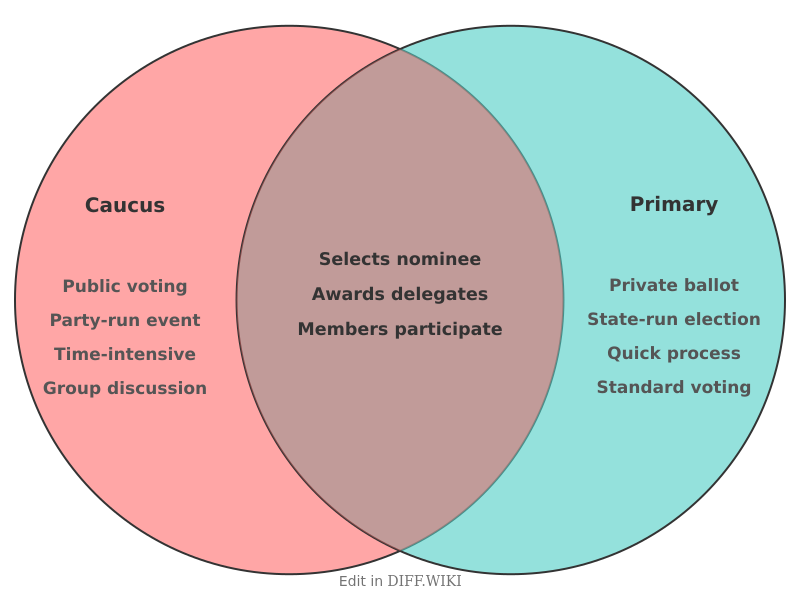
In United States presidential elections, a caucus and a primary are the two main methods political parties use to select their nominee for a general election.[1][2] While both serve to allocate delegates who will vote for a candidate at a national party convention, their processes differ significantly.[3][4] Caucuses are private meetings run by political parties, while primaries are state-run elections.[5]
Historically, caucuses were the dominant method for choosing nominees, but most states now use primaries.[1][4] The shift toward primaries began in the Progressive Era of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, driven by a movement to increase voter participation in the nomination process.[1]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Caucus | Primary |
|---|---|---|
| Administration | Run by state political parties. | Run by state and local governments.[5] |
| Format | In-person meetings at a set time and place. Activities include discussion and debate among participants.[4] | Standard election process where voters cast a secret ballot.[4] Polling places are open for most of the day. |
| Voting Method | Varies by party. Can be a secret ballot, a public show of hands, or by dividing into groups.[4] | Anonymous, secret ballot. |
| Time Commitment | Often requires several hours of participation. | Typically takes only a few minutes to cast a ballot.[5] |
| Voter Participation | Turnout is generally lower due to the higher time commitment. | Higher turnout because it is more accessible and less time-consuming.[5] |
| Voter Eligibility | Rules are set by the party and often require party membership.[3] | Rules are set by the state. Can be open (any registered voter), closed (only registered party members), or a hybrid. |
Caucus Process[edit]
A caucus is a gathering of party members at a specific time and place, such as a school or community center, to openly select a candidate. The format is a public event where representatives for candidates may give speeches, and participants can debate and try to persuade others.
Voting methods in caucuses vary. Some use a secret ballot, but others are more public. For example, some Democratic caucuses have involved voters physically dividing into groups based on their preferred candidate.[3] In this system, if a candidate does not meet a certain threshold of support (often 15%), their supporters must realign with another candidate.[3] This public process continues until viable candidate groups are established.[3]
Primary Process[edit]
A primary election is administered by state and local governments and resembles a general election. Voters go to a polling place and cast a secret ballot for their preferred candidate.[4] The process is anonymous and does not involve public discussion or persuasion at the polling site.
There are several types of primaries, and the rules differ by state.
- Closed Primary: Voters must be registered with a specific political party to vote in that party's primary.
- Open Primary: A registered voter can participate in any party's primary, regardless of their own party affiliation.
- Semi-closed or Semi-open: These are variations. For example, a state might allow unaffiliated voters to participate in the primary of their choice, while voters registered with a party may only vote in that party's primary.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "dictionary.com". Retrieved December 20, 2025.
- ↑ "steubencountyny.gov". Retrieved December 20, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "polyas.com". Retrieved December 20, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 "ballotpedia.org". Retrieved December 20, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "ucdenver.edu". Retrieved December 20, 2025.