Differences between Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
Contents
Cellular Respiration vs. Photosynthesis[edit]
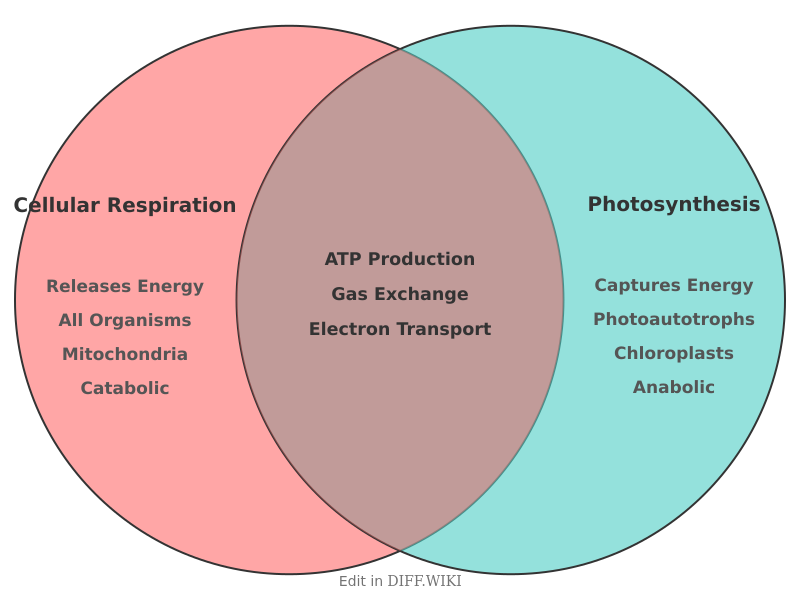
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are complementary biological processes that are essential for life on Earth.[1] Photosynthesis uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.[2] Cellular respiration, conversely, breaks down glucose and other organic molecules to release energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), producing carbon dioxide and water as waste products.[3] Together, these two processes facilitate the flow of energy and the cycling of key elements through the biosphere.[2]
Comparison Table[edit]
[1]| Energy Flow || Exergonic (releases energy). || Endergonic (requires energy).| Category | Cellular Respiration | Photosynthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To release energy stored in glucose for cellular activities (ATP production).[4] | To capture light energy and store it in the chemical bonds of glucose (food production).[5] |
| Organisms | Occurs in all living organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. | Occurs in photoautotrophs, such as plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. |
| Location in Eukaryotic Cell | Cytoplasm (glycolysis) and mitochondria.[1] | Chloroplasts.[2] |
| Reactants | Glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2). | Carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and light energy. |
| Products | Carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and ATP. | Glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2). |
| Chemical Equation | [1]| 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 | |
| Metabolic Process | Catabolic (breaks down large molecules into smaller ones). | Anabolic[5] (builds large molecules from smaller ones). |
Relationship Between Processes[edit]
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected, with the products of one process serving as the reactants for the other. Photosynthesis generates glucose and oxygen, which are the essential inputs for aerobic cellular respiration. In turn, cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide and water, which are the necessary reactants for photosynthesis. This[4] cyclical relationship is fundamental to the balance of gases in the Earth's atmosphere and the continuous flow of energy that sustains ecosystems.
Plants perform both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. They[1] create their own food via photosynthesis and then break down that glucose through respiration to produce ATP for their cellular functions, such as growth and development. Animals and other heterotrophs, which cannot produce their own food, depend on the glucose produced by photosynthetic organisms for their energy needs, which they unlock through cellular respiration.[1]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "visiblebody.com". Retrieved December 25, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "orau.gov". Retrieved December 25, 2025.
- ↑ "britannica.com". Retrieved December 25, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "study.com". Retrieved December 25, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "quora.com". Retrieved December 25, 2025.