Differences between Celsius and Fahrenheit
Contents
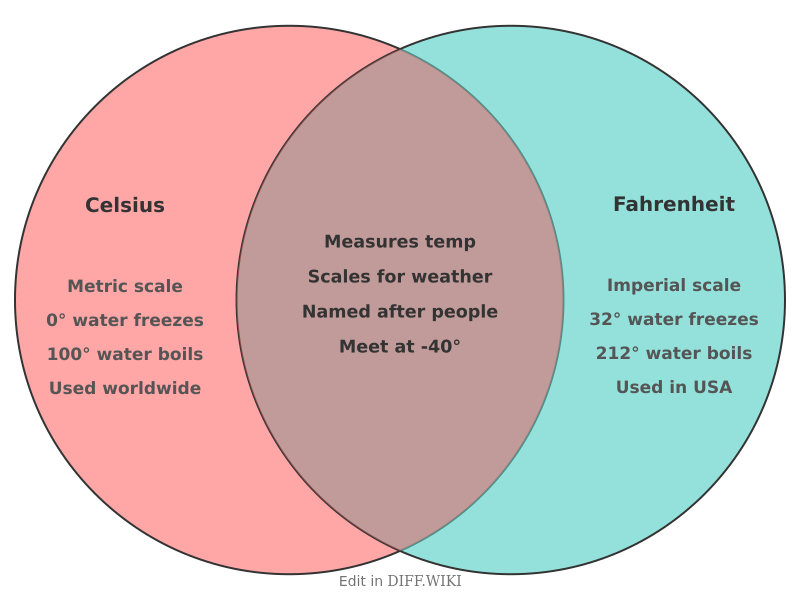
Celsius vs. Fahrenheit[edit]
Celsius and Fahrenheit are two temperature scales used to measure temperature.[1] The Celsius scale is the most common temperature scale in the world, while Fahrenheit is still in everyday use in the United States and some other countries.[2][3][4] The scales are based on the freezing and boiling points of water, though with different numerical values.[1]
History[edit]
The Fahrenheit scale was introduced in 1724 by the German-Dutch physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit.[2][5] He based his scale on a few reference points, including the temperature of a brine solution, the freezing point of water, and what he approximated as human body temperature. The scale was later adjusted to set the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F.
The Celsius scale was created in 1742 by the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius. Originally, Celsius designated 0° for the boiling point of water and 100° for the freezing point. A year later, the scale was inverted to its present form by Jean-Pierre Christin, establishing 0°C as the freezing point and 100°C as the boiling point of water. The scale was known as "centigrade" until 1948 when it was officially named Celsius.
Comparison[2][4] Table[edit]
| Category | Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Inventor | Anders Celsius | Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit |
| Year of Invention | 1742 | 1724 |
| Freezing Point of Water | 0°C | 32°F |
| Boiling Point of Water | 100°C | 212°F |
| Interval Between Freezing and Boiling | 100 degrees | 180 degrees |
| Absolute Zero | -273.15°C | -459.67°F |
| Primary Modern Usage | Worldwide | United States and its territories, Cayman Islands, Liberia, Bahamas, Belize |
| Conversion[4] to other unit | °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32 | °C = (°F − 32) × 5/9 |
Usage[edit]
The Celsius scale is used by the majority of countries worldwide. It is the standard for most scientific and international applications. The Fahrenheit scale remains the primary scale for daily use in the United States, its territories, and a few other nations. In some countries, like[4] the United Kingdom and Canada, Fahrenheit may still be seen alongside Celsius, particularly among older generations or for specific purposes like cooking.
Conversion[edit]
The relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit is linear. The two scales are equal[1] at -40 degrees, where -40°C is the same as -40°F. To convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit, one can multiply the Celsius temperature by 9/5 and then add 32. To convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius, subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature and then multiply by 5/9.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "byjus.com". Retrieved November 07, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "brannan.co.uk". Retrieved November 07, 2025.
- ↑ "foxweather.com". Retrieved November 07, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "earthdate.org". Retrieved November 07, 2025.
- ↑ "ebsco.com". Retrieved November 07, 2025.