Differences between Compound and Element
Contents
Comparison Article[edit]
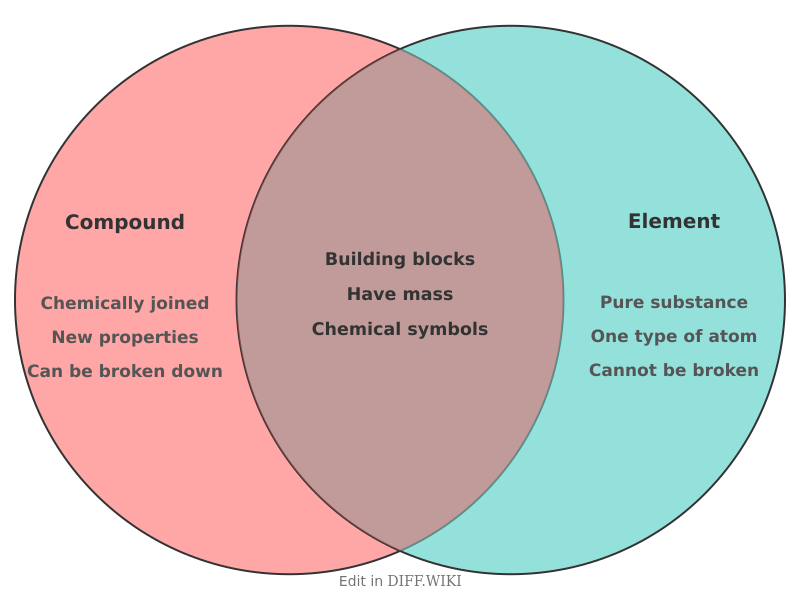
In chemistry, all matter is classified into a few fundamental categories. Among the purest forms are elements and compounds. An element is a pure substance consisting of only one type of atom, identified by its unique number of protons, known as its atomic number.[1][2] A chemical compound is a substance formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio.[3][4] While both are pure substances, the primary distinction lies in their composition and the fact that compounds can be broken down into their constituent elements, whereas elements cannot be simplified further by chemical reactions.[1][4]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Element | Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Unit | Atom[5] | Molecule or formula unit |
| Composition | Consists of only one type of atom | Consists of two or more types of atoms from different elements |
| Chemical Bonds | Atoms are not chemically bonded to different elements | Atoms of different elements are joined by chemical bonds (e.g., covalent or ionic) |
| Separation | Cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means[2][4] | Can be separated into its constituent elements through chemical reactions |
| Representation | A chemical symbol (e.g., H, O, Fe) | A chemical formula (e.g., H₂O, NaCl, C₆H₁₂O₆) |
| Total Number | 118 known elements | Millions[1] of different compounds have been identified |
| Properties | Has a unique set of physical and chemical properties | Properties are different from those of its constituent elements |
Chemical[5] formation and decomposition[edit]
Compounds are formed from elements through chemical reactions. During these reactions, atoms of the constituent elements rearrange and form new chemical bonds, creating a new substance with a fixed composition. For example,[5] iron (Fe), an element, can react with sulfur (S), another element, to form the compound iron sulfide (FeS).
The process[5] can also be reversed. A compound can be broken down, or decomposed, into its individual elements, but this requires a chemical change, often involving energy. A common example is the electrolysis of water (H₂O). By passing an electric current through water, the chemical bonds between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms are broken, releasing hydrogen gas (H₂) and oxygen gas (O₂), the elements from which the compound was formed.
Properties[edit]
A significant difference between elements and compounds is that a compound's properties are unique and distinct from the properties of its component elements. This transformation occurs because the chemical bonding between atoms fundamentally changes the substance's structure and behavior.
A well-known example is sodium chloride (NaCl), or table salt. It is a compound formed from two elements:
- **Sodium (Na)**: A soft, highly reactive metal that reacts violently with water.
- **Chlorine (Cl)**: A poisonous, yellow-green gas.
When chemically combined, they form sodium chloride, a stable, white crystalline solid that is essential for human life. The dangerous properties of the individual elements are not present in the resulting compound. This illustrates that when elements form compounds, they lose their individual properties and create a new substance with an entirely new set of characteristics.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "britannica.com". Retrieved October 30, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "byjus.com". Retrieved October 30, 2025.
- ↑ "quora.com". Retrieved October 30, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "preply.com". Retrieved October 30, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "rsc.org". Retrieved October 30, 2025.