Differences between Crab and Lobster
Contents
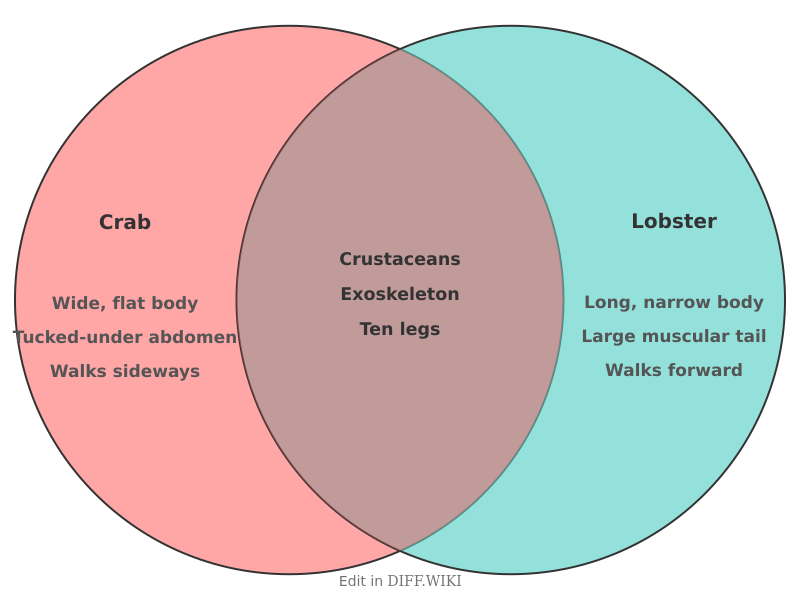
Crab vs. Lobster[edit]
Crabs and lobsters are crustaceans belonging to the order Decapoda, meaning they both have ten legs.[1] Despite this shared classification, they exhibit significant differences in their anatomy, habitat, and life history. Both are economically important as seafood.[2]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Crab | Lobster |
|---|---|---|
| Body Structure | Broad, rounded carapace with a small abdomen tucked underneath.[3] | Elongated, cylindrical body with a long, muscular tail.[4] |
| Locomotion | Primarily walks sideways.[5] | Walks forward and swims backward by flexing its tail.[2] |
| Claws | One pair of claws, which can be of different sizes in some species. | Three of their five pairs of legs have claws, with the first pair being significantly larger.[2] |
| Habitat | Found in saltwater, freshwater, and terrestrial environments, from shorelines to deep sea. | Primarily saltwater creatures, living in burrows or crevices on the sea floor.[2] |
| Lifespan | Varies greatly by species, from a few years to over 100 for the Japanese spider crab. | Can be very long-lived, with some individuals estimated to live over 70 years. |
| Diet | Omnivorous, feeding on algae, bacteria, mollusks, and other small animals. | Omnivorous, but with a diet that often includes more animals like fish, sea urchins, and even other crustaceans.[4] |
| Social Behavior | Varies from solitary to social, with some species known to cooperate. | Generally solitary creatures that live alone in shelters. |
| Taste and Texture | The meat is typically sweet and has a flaky texture. | The meat is also sweet, sometimes described as a mix of crab and shrimp, with a firmer, denser texture. |
Anatomy and Morphology[edit]
The most apparent distinction between crabs and lobsters is their body shape. Crabs possess a wide carapace and a short abdomen that is folded under the thorax.[3] Lobsters, in contrast, have a more elongated body with a prominent, muscular tail that is used for rapid backward propulsion, a behavior known as the caridoid escape reaction.[2]
While both are decapods, the arrangement of their legs and claws differs. In crabs, the front pair of their ten legs are modified into claws, called chelae. Lobsters have claws on the first three pairs of their legs, with the front pair being much larger and specialized—one for crushing and one for tearing or cutting. Another[2] difference is their antennae; lobsters have very long antennae, while those of crabs are short.
Habitat and Behavior[edit]
Crabs are highly adaptable and inhabit a wide range of environments, including oceans, freshwater bodies, and even land. Lobsters[1] are almost exclusively marine, typically found on the sea floor in rocky, sandy, or muddy areas where they can dig burrows or find shelter.
In[1] terms of behavior, lobsters are typically solitary animals. Crabs exhibit a wider range of social behaviors; while many are solitary, some species display complex social interactions and cooperation. Their methods of locomotion are also distinct, with most crabs known for their sideways scuttling, while lobsters walk forward and swim backward.
[5][2]=== Lifespan and Diet === Lifespans vary significantly among crab species. Smaller crabs may only live for three to four years, whereas larger species like the Japanese spider crab can live for up to a century. Lobsters are known for their longevity, often exceeding 70 years in the wild.
Both are omnivores and scavengers. Crabs[4] consume a varied diet that includes algae, fungi, bacteria, and small mollusks. Lobsters also have a broad diet but tend to be more predatory, consuming other crustaceans, sea urchins, and small fish.[4]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "deepseaworld.com". Retrieved November 19, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved November 19, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "ebsco.com". Retrieved November 19, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "mychicagosteak.com". Retrieved November 19, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "redcrabseafood.com". Retrieved November 19, 2025.