Differences between DDS and DMD
DDS vs. DMD[edit]
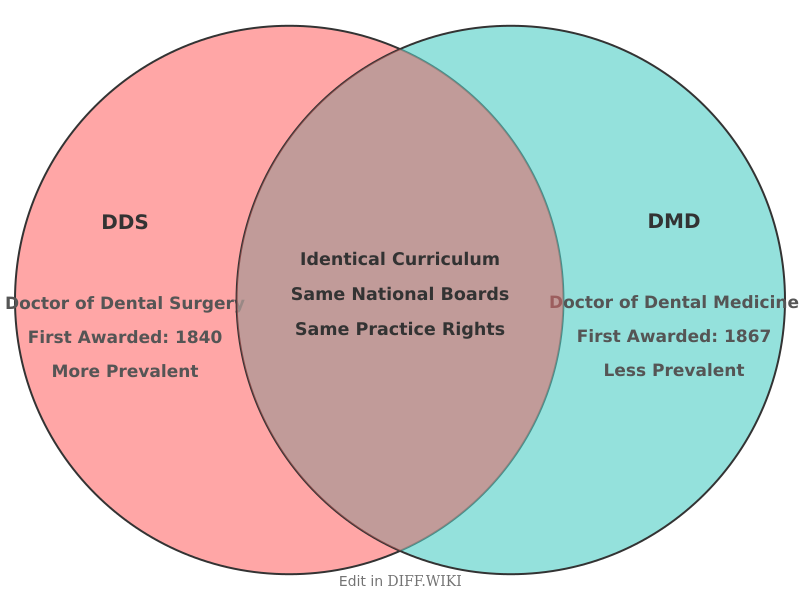
When seeking dental care, patients may notice that dentists have either DDS or DMD listed after their names. DDS stands for Doctor of Dental Surgery, while DMD stands for Doctor of Dental Medicine.[1][2] Despite the different names, the American Dental Association (ADA) states that the two degrees are the same and that dentists with either a DDS or DMD have received the same education.[3][4] The distinction between the two degrees is purely historical and depends on the university that awarded it.[5]
The educational requirements for both DDS and DMD degrees are identical. Aspiring dentists must complete a four-year undergraduate degree, typically with a focus on science, before entering a four-year accredited dental school.[2] The curriculum in dental school is standardized by the Commission on Dental Accreditation (CODA). It includes two years of biomedical sciences followed by two years of hands-on clinical and laboratory training.[2] Upon graduation, all dentists, regardless of their degree title, must pass the same National Board Dental Examination and a regional clinical board examination to become licensed to practice.[2]
The difference in the degree names originated in the 19th century. The first dental school, the Baltimore College of Dental Surgery, was established in 1840 and awarded the DDS degree. Later, in 1867, Harvard University established its dental school and chose to grant a DMD degree, from the Latin "Dentariae Medicinae Doctor," to align with its tradition of Latin degree names. Other universities then had the option to award either a DDS or a DMD. Currently, about two-thirds of dental schools in the United States award the DDS degree, while the remaining one-third award the DMD.
Both DDS and DMD graduates are qualified to practice general dentistry, which includes a wide range of procedures from routine cleanings to extractions and root canals. Neither degree is considered more prestigious than the other, and state licensing boards recognize them as equivalent.[3]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | DDS | DMD |
|---|---|---|
| Full Title | Doctor of Dental Surgery | Doctor of Dental Medicine[1][2] |
| First Awarded | 1840 by the Baltimore College of Dental Surgery | 1867 by Harvard University |
| Accrediting Body | Commission on Dental Accreditation (CODA) | Commission on Dental Accreditation (CODA) |
| Curriculum | Identical to DMD; includes two years of biomedical sciences and two years of clinical training | Identical to DDS; includes two years of biomedical sciences and two years of clinical training[2] |
| National Boards | National Board Dental Examination | National Board Dental Examination[2] |
| Practice Rights | Licensed to practice general dentistry | Licensed to practice general dentistry |
| Prevalence | Awarded by approximately two-thirds of U.S. dental schools | Awarded by approximately one-third of U.S. dental schools |
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "ifdww.com". Retrieved January 10, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 "colgate.com". Retrieved January 10, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "shemmassianconsulting.com". Retrieved January 10, 2026.
- ↑ "mouthhealthy.org". Retrieved January 10, 2026.
- ↑ "amitydentistry.com". Retrieved January 10, 2026.