Differences between Earthworm and Leech
Earthworm vs. Leech[edit]
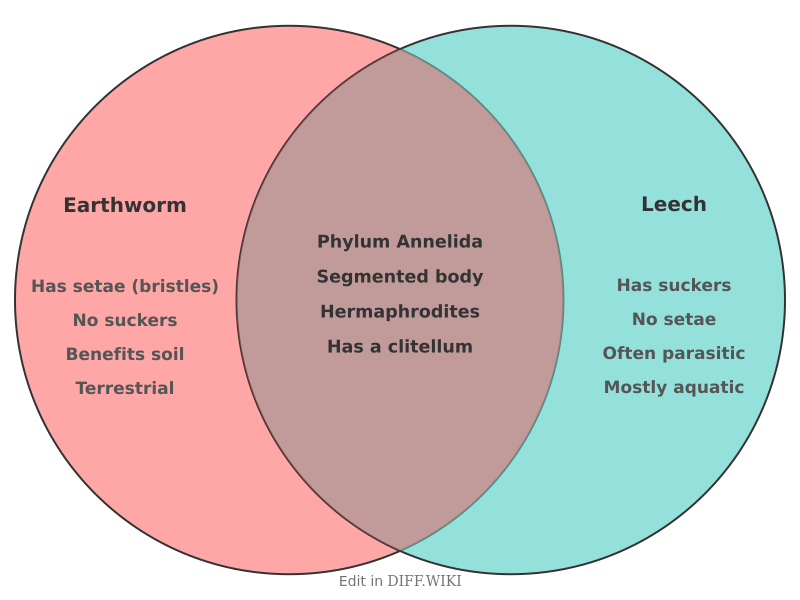
Earthworms and leeches are segmented worms belonging to the phylum Annelida and the class Clitellata, indicating a close evolutionary relationship.[1][2] Both groups are characterized by the presence of a clitellum, a glandular section of the body that secretes a cocoon for eggs.[1] Despite these similarities, they belong to different subclasses and exhibit significant differences in their anatomy, habitat, and feeding habits.[3] Earthworms are in the subclass Oligochaeta, while leeches belong to the subclass Hirudinea.[3][1]
Earthworms are primarily terrestrial, inhabiting soils where they contribute to aeration and nutrient cycling.[4][5] In contrast, most leech species are found in freshwater environments, though some are terrestrial or marine.[3][2] A key physical distinction is the presence of suckers on leeches, typically one at each end of their flattened body, which they use for attachment and movement.[2] Earthworms have a more cylindrical body shape and lack suckers, instead using small bristles called setae for locomotion. Leeches do not have setae.[1]
Their diets are also markedly different. Earthworms are detritivores, consuming decomposing organic matter in the soil.[3] While many leeches are predatory, feeding on small invertebrates, some are well-known for being parasitic, feeding on the blood of vertebrates.[4] Parasitic leeches produce an anticoagulant called hirudin in their saliva to prevent the host's blood from clotting.[4]
Both earthworms and leeches are hermaphrodites, possessing both male and female reproductive organs.[1] However, a key difference in their reproductive biology is the clitellum. In earthworms, the clitellum is a permanent feature of the adult worm, while in leeches, it is only present during the reproductive season.[1]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Earthworm | Leech |
|---|---|---|
| Subclass | Oligochaeta[3] | Hirudinea[3] |
| Body Shape | Cylindrical | Dorso-ventrally flattened[1] |
| Suckers | Absent | Present at anterior and posterior ends[2] |
| Setae | Present | Absent[1] |
| Habitat | Mostly terrestrial (soil)[4] | Mostly freshwater, some terrestrial or marine[3][2] |
| Diet | Detritivore (decomposing organic matter)[3] | Predator or parasite (blood)[4] |
| Clitellum | Permanent in adults | Appears only during breeding season[1] |
| Circulatory System | Closed | Open |
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "australian.museum". Retrieved January 07, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 07, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 07, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "differencebetween.info". Retrieved January 07, 2026.
- ↑ "difference.wiki". Retrieved January 07, 2026.